Developers have been using Android Studio for developing apps which cater to several use cases. They mostly use Java or Kotlin for native app development. Java has several open-source tools and libraries that prove helpful for developers. Kotlin can introduce new solutions to prevalent use cases and enhance the Java ecosystem.
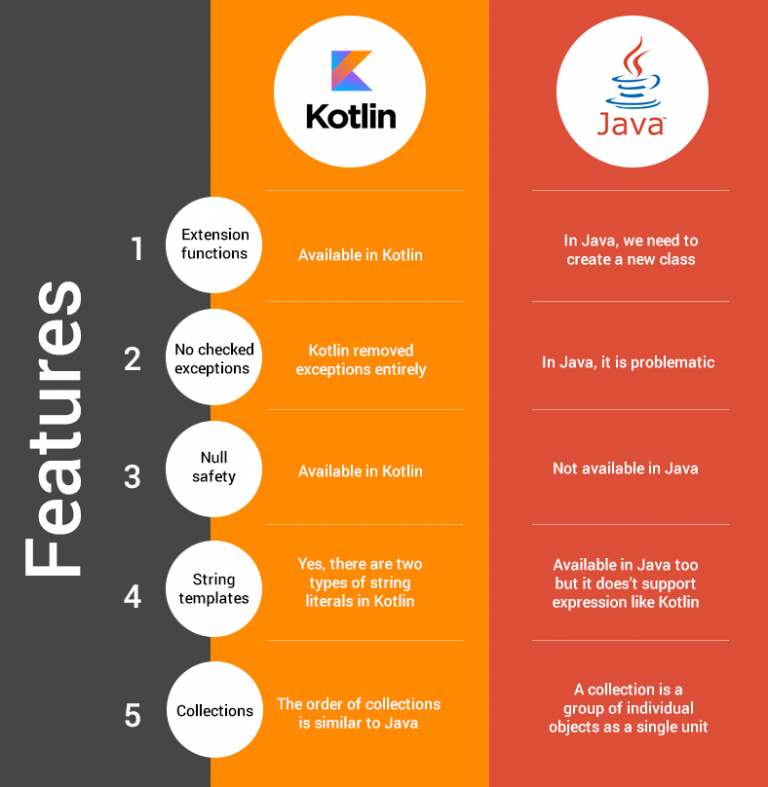
Kotlin has gradually grown as the language of choice among the developer community. Several developers prefer Kotlin as it is precise, and it can make life easier for them as it reduces the risk of errors. There is an inbuilt null safety feature, and it is interoperable with Java.
We will discuss more the importance of Java and Kotlin in Android Studio Native app development.
Importance of using Java

The prime importance of Android development arises from the need to design a platform-agnostic application which can run on any device. It can run on a unique virtual machine and on all devices on which it is loaded. Java has extensive libraries, and developers can quickly leverage them. The Android SDK has several Java libraries. Several resources have proficiency in the language. They can help design and improve applications with several libraries and Java tools.
Importance of using Kotlin

Kotlin is another option available for Android development. Developers can write code faster, and it is a statically typed language. It ensures code security and enhances developer productivity. You can focus on creating quality code without concentrating on the boilerplate areas. It is fully interoperable with Java too.
When you are using Kotlin, you can easily avoid NullPointerExceptions due to the presence of @NonNull and @Nullable in the type system. When you use Kotlin, the applications are less likely to crash. It can streamline asynchronous programming and request database updates and network calls.
Critical features in Kotlin
Declaring Variable
You can declare variables using two keywords: “val” and “var.”
Use “val” for variables whose values do not change. Once declared with “val,” you cannot reassign a value to the variable.
Use “var” for variables whose values can change over time.
Null Safety
You can declare a reference type variable without providing any initial explicit value. Here, the variables can have a null value. Remember that variables in Kotlin can’t hold null values by default. The nullable variables must be handled carefully to prevent any NullPointerException.
Conditional logic
You can deploy conditional logic in several ways. In an if-else statement, if the expression wrapped in parentheses next to the “if” keyword evaluates to true, the code in that branch executes. Otherwise, the code in the “else” part executes.
Functions
Several expressions can be grouped into a function. It is better to have the expressions in a function and call the function when needed. You can use the fun keyword and have the function name after that. The body is where you can define the expressions and call them when you invoke the function. When declaring a function, you can specify several arguments and their types.
Simplify function declarations
You can use the generateAnswerString() function as it is simple. It can declare a variable and return it immediately. The result of the expression is returned from the function, and you can skip declaring the local variable directly. The assignment operator can replace the return keyword.
Higher order functions
A function in Kotlin can also take another in an argument. They are called higher order functions. It can help communication, like using a callback interface in Java. The stringMapper() function can take a String with the function to derive an Int value from the String, which you can pass into it.
Classes
If you want to add your type, you can use a class. The class will represent the state with properties. You can declare a class using the “class” keyword. The property is a class-level variable with a setter, getter, and a backing field. The functions can modify the state and help expose the required data.
SAM conversion
You can implement the OneClickListener interface and listen for click events in Android. It has a single abstract method, oneClick(), which you must implement. You can use SAM conversion for cleaner code. For example, setOnClickListener() will take OnClickListener as argument. OnClickListener has the same single abstract method and you can represent them as an anonymous function in Kotlin. This is called the Single Abstract method (SAM) conversion.
Companion objects
The companion objects can define functions or variables which you can conceptually link to a type. However, you can tie them to any particular object. They are like Java’s static keywords for methods and variables. You can define TAG at the file’s top level. But, the file can itself have several functions, variables, and classes.
FAQs
1. What is native development in Android Studio?
Native development in Android Studio refers to creating Android apps using the programming languages officially supported by the Android platform, which are Java and Kotlin. These languages allow developers to access the full range of Android APIs and services, enabling the creation of high-performance and deeply integrated Android applications.
2. How do Java and Kotlin differ in Android development?
Java has been the traditional language for Android development, known for its portability, ease of debugging, and widespread use. Kotlin, on the other hand, is a newer language designed to interoperate fully with Java while offering additional safety features, such as null safety, and a more concise syntax. Kotlin is now the recommended language for new Android projects due to its expressive syntax, reducing boilerplate code and improving developer productivity.
3. Can Java and Kotlin code coexist in the same Android Studio project?
Yes, Java and Kotlin code can coexist within the same Android Studio project, allowing developers to gradually migrate to Kotlin at their own pace or to use both languages where they see fit. Android Studio provides tooling support for converting Java code to Kotlin, helping to streamline the migration process.
4. How do I start a new Android project in Kotlin in Android Studio?
To start a new project in Kotlin in Android Studio:
- Open Android Studio and click on “Start a new Android Studio project.”
- Choose your desired project template and click “Next.”
- Fill in your project details, such as name and save location.
- Make sure the “Language” option is set to “Kotlin.”
- Configure any additional project settings, then click “Finish” to create your project.
5. What are the benefits of using Kotlin for Android development?
Benefits of using Kotlin for Android development include:
- Conciseness: Kotlin reduces boilerplate code, making code more readable and maintainable.
- Safety: Kotlin’s null safety features help prevent null pointer exceptions, a common source of runtime crashes in Java.
- Interoperability: Kotlin is fully interoperable with Java, allowing the use of existing Java libraries and frameworks in Kotlin projects.
- Tool Support: Kotlin is fully supported in Android Studio, offering advanced coding assistance, debugging, and refactoring tools.
6. Are there any performance differences between apps written in Java and Kotlin?
The performance of apps written in Kotlin is generally on par with those written in Java, as both languages compile to the same bytecode. However, Kotlin’s language features can lead to more efficient code patterns that may improve app performance indirectly. Any performance differences are usually minimal and not noticeable to the end-user.
7. How can I migrate my existing Java Android application to Kotlin?
To migrate your existing Java application to Kotlin in Android Studio:
- Open your Java file in Android Studio.
- Navigate to “Code” > “Convert Java File to Kotlin File” in the menu bar, or use the shortcut
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+K(on Windows) orCmd+Option+Shift+K(on Mac). - Android Studio will automatically convert the file to Kotlin and highlight any issues or suggested changes.
- Review and test your newly converted Kotlin code to ensure it behaves as expected.
Migrating to Kotlin can be done gradually, file by file, allowing you to test and adjust your codebase incrementally.