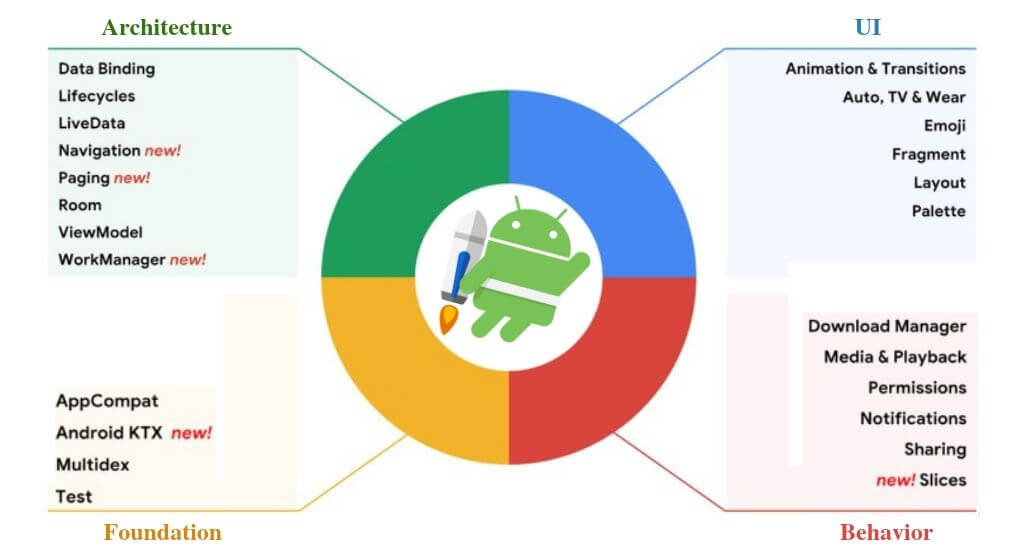
Jetpack is a suite of libraries which helps the developers adhere to industry best practices. It can help minimise the need for boilerplate code. You can write code which is consistent across Android versions and devices.
(Source: https://developer.android.com/jetpack)
WindowManager
You can use the WindowManager library for supporting various device form factors.
Unbundling the WindowManager

You can optimise the application for large screen devices and foldables.
The screen sizes in Android change fast, and as foldables and tablets are seeing increased use, developers must understand the state and size of the app soon. It is essential to develop a responsive UI. The WindowManager is in the Beta stage. It provides features like the Android framework WindowManager and supports callback adapters to screen changes, responsive UIs, and window testing APIs.
The new APIs include:
- FoldingFeature: Developers can monitor the folded state of the device and understand the device postures.
- WindowLayoutInfo: It has the display features of a window. It informs you whether the window has a hinge or fold.
- WindowMetrics: Gives the overall display metrics or the current window metrics.
It allows faster iteration on APIs and supports the changing device market. Developers can accept updates to the library without waiting for the latest Android versions.
The developers can adopt Jetpack WindowManager through testing APIs and device-agnostic APIs, allowing WindowMetrics to respond effortlessly to any changes in window size. The developers can focus only on building great experiences on these devices. The Jetpack WindowManager can support feature detection for API 14.
The library
The Jetpack WindowManager is a modernised Kotlin-first library. It can readily support new device form factors. It provides “AppCompat-like” features for building applications using a responsive UI.
Fold states
Apps can receive the events if there is any change in the device’s fold state. It allows an update in the UI to support new user interactions. A collection of Android libraries which help them provide backwards compatibility and incorporate best practices in the apps.
Using the Jetpack library in your app
The Jetpack components are available on the Google Maven repository. You can open the settings.gradle file and add the google() repository in the dependencyResolutionManagement { repositories {…}} block. It is then possible to add the Jetpack components, like architecture components ViewModel and LiveData, in the module’s build.gradle file.
Many Jetpack libraries can provide the Android KTX extensions by using lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx and lifecycle-livedata-ktx.
Take advantage of Jetpack
The Jetpack libraries can be used in combination or alone to meet various app needs.
The WorkManager is used for various background scheduling needs.
There is ample area for data storage persistence.
Navigation can help manage the application navigation flow.
CameraX can help you with the camera app needs.
The Jetpack libraries are published in the androidx namespace.
Migrating to Paging 3
Paging 3 is different from the earlier versions of the Paging library. The current version can provide enhanced features and focus on typical difficulties using Paging 2.
Benefits of migrating to Paging 3
The Paging 3 module covers the following features:
Provision for async loading using Guava ListenableFuture or RxJava Single primitives.
- First-class support for Kotlin Flow and coroutines.
- Enhancements to the repository layer, including a simplified data source interface and cancellation support.
- Built-in error signals and load state to ensure responsive UI design. It also covers refresh and retry functionalities.
- There are improvements to the list separators, presentation layer, loading state headers and footers, and custom page transforms.
The watch face is a common visible way used by people articulate themselves on the smartwatches. They are also among of the finest ways to present your brand to your users.
Migrating the app to Paging 3
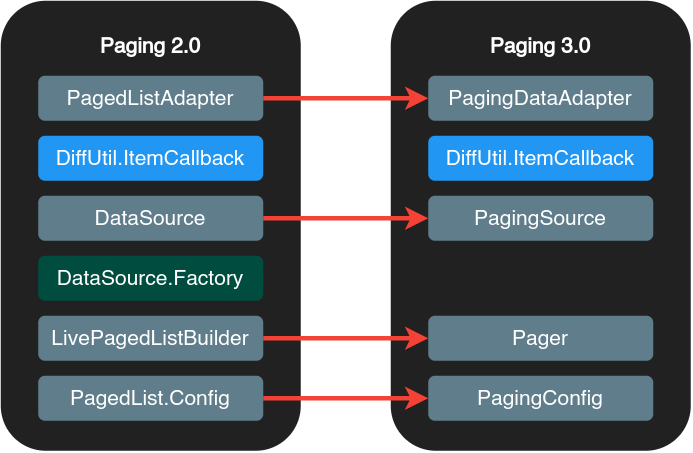
If you want to move to Paging 3 fully, it becomes essential to migrate all the three main modules from Paging 2:
- DataSource classes
- PagedList
- PagedListAdapter
There are some Paging 3 components which are backwards-compatible with earlier Paging versions. Paging 3 has the PagingSource API which can be an ideal data source for RxPagedListBuilder and LivePagedListBuilder from older versions. Older DataSource objects can be used with Pager API and toPagingSourceFactory() method.
You will have the following migration options:
- Migrate the PagedListAdapter and PagedList. Continue to use the older DataSource API.
- Migrate the DataSource to PagingSource. Leave the remainder of the Paging implementation unchanged.
- Migrate the entire Paging implementation and migrate the app entirely to Paging 3.
Wear Watchface 1.0
Wear Watchface is a new library for developing WearOS watch faces. The Watch Face Studio from Samsung is an excellent tool for creating watch faces with no code. It covers all features from Wearable Support Library, including the new features making it simpler for supporting customisation. Some of them are:
- Provides a WYSIWYG watch face structure UI on the device.
- Separate, smaller libraries.
- Watch face styling that exists across the watch and phone.
- Battery enhancements through improved battery usage models.
- Innovative screenshot APIs for users to see samples of the watch face alterations in real-time.
(Source: https://android-developers.googleblog.com/2021/12/develop-watch-faces-with-stable-jetpack.html)
FAQs
1. What is Android Jetpack?
Android Jetpack is a suite of libraries and tools designed to help developers follow best practices, reduce boilerplate code, and write code that is consistent across Android versions and devices. It includes components for the architecture, UI, and behavior of an app, ensuring that developers have everything they need to make their apps robust and efficient.
2. What is AndroidX and how is it related to Jetpack?
AndroidX is a major part of Android Jetpack, representing a newer set of libraries that is backward-compatible and provides more consistent and streamlined development. It is essentially a rebranding and improvement of the original Android Support Library, offering finely-grained libraries and modular components that make it easier for developers to maintain and update their apps.
3. What are some of the key components of Android Jetpack?
Some of the key components of Android Jetpack include:
- Lifecycle (managing your UI component lifecycle easily)
- LiveData (building data objects that notify views when the underlying database changes)
- Navigation (handling everything needed for in-app navigation)
- Room (a layer on top of SQLite designed for fluent database access while harnessing the full power of SQLite)
- ViewModel (designed to store and manage UI-related data in a lifecycle-conscious way)
- WorkManager (for managing background tasks in an optimal way)
4. Why should developers use Jetpack and AndroidX libraries in their projects?
Using Jetpack and AndroidX libraries provides numerous benefits, such as reducing boilerplate code, following best practices by design, and compatibility across different versions of Android. These libraries are also continuously updated with improvements and new features, ensuring that apps built with them are modern and efficient.
5. Can I migrate an existing app to Jetpack and AndroidX?
Yes, you can migrate an existing app to use Jetpack and AndroidX libraries. Android Studio offers a refactoring tool to help with the migration. However, it’s important to test your app thoroughly after migration to catch any potential issues that may arise from library changes.
6. Where can I find resources and documentation for Android Jetpack and AndroidX?
The official Android Developers website is the best resource for finding documentation on Android Jetpack and AndroidX. It offers guides, reference documentation, and code samples to help you understand and implement the components in your apps. Additionally, there are numerous community tutorials, videos, and articles available online that provide practical advice and examples.