Debugging and building your app can be a daunting task. You want to make sure that your application is running as smoothly as possible, but every time you make a change you run the risk of introducing errors. This blog post provides some tips on how to debug your app and make changes without introducing errors. From setting up your development environment to debugging tools, read on to learn everything you need to know to build and debug your app successfully.
What is a Debugging Process?
Image Source: Link
A debugging process for software development is the systematic investigation of a system in order to identify and correct errors. Debugging is typically divided into two phases: pre-debugging and debugging.
Pre-debugging activities include identifying the problem, determining its cause, and designing a plan to solve it. This involves understanding the system design, analyzing data flows, and understanding how the software behaves. Once the problem has been identified, debugging begins with systematically testing hypotheses to find the source of the error. Debugging can also involve modifying or enhancing code to confirm that it works as intended.
Once you find an error, fixing it requires knowledge of both the codebase and how it interacts with other parts of the system. Reaching a solution often requires taking multiple steps: verifying that the fix works as intended, making sure that all affected systems are updated, and documenting changes so that future developers can reproduce the issue if necessary.
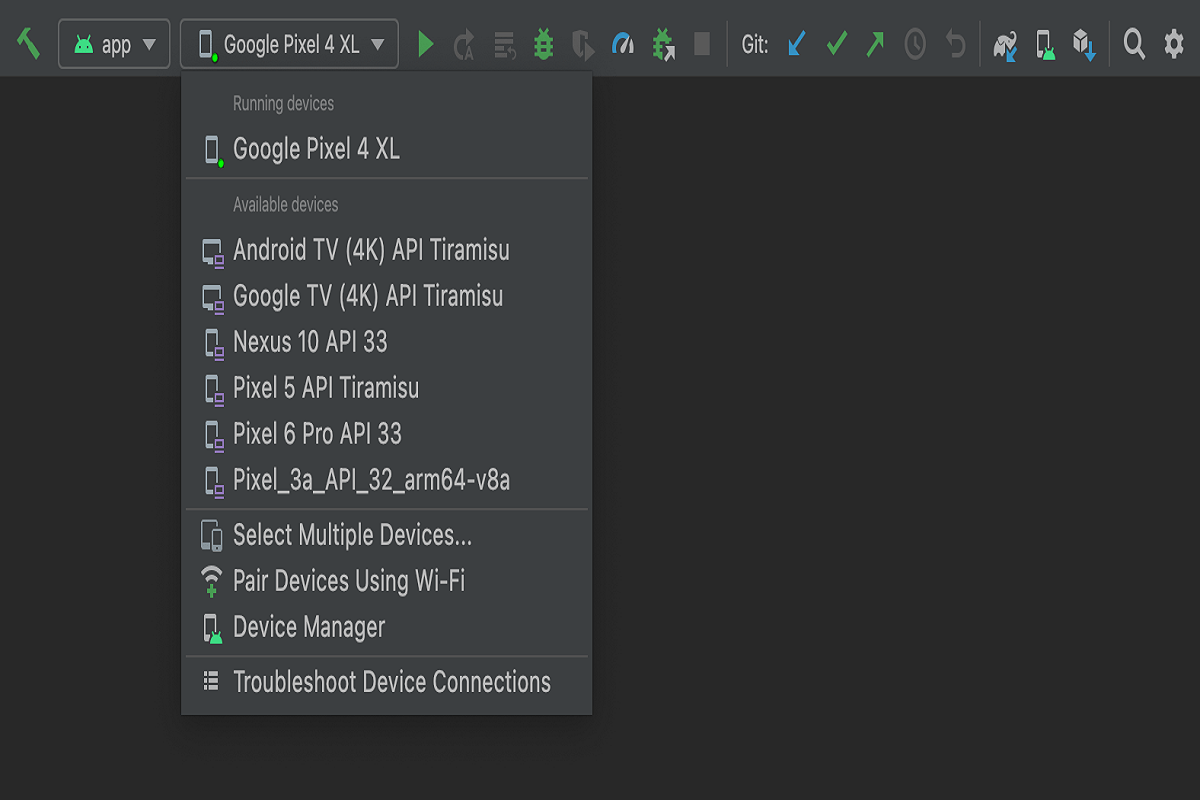
How to Debug Your App?
If you are having trouble debugging your app or building it, there are a few things you can do to help.
First, make sure you have the correct version of the SDK and tools installed. The SDK comes with a debug build of Android Studio which makes debugging and building much easier.
Second, try to break your app in a way that is specific to your problem. This will help you pinpoint where the issue lies.
Third, use logging and profiling to see where your app is spending its time and how it is behaving. This information can be helpful in diagnosing and fixing issues. Additionally,logging can help you track down errors that might not show up in normal execution traces.
Fourth, search for answers on Stack Overflow or Google Groups related to your problem. There are likely people out there who have encountered the same issue before and may have some good advice on how to solve it.
Finally, post your question on Stack Overflow or Google Groups with the tag “android” so that others might find it too.
What are the Different Types of Debugging Tools?
You can divide debugging tools into three categories:
- Functional debugging – You can use it to find and fix errors in your code that have nothing to do with the user interface. Moreover, you can use it for things like finding where a function is calling too many times or checking that a variable is being set correctly.
- Performance debugging – You can use this to find and fix errors that affect the speed of your app. It can track down issues like slow network connections or memory leaks.
- User experience debugging – You can use this to find and fix errors that affect how the user interacts with your app. It can identify problems with how your controls look or how your menus work.
Testing and Debugging Your Application
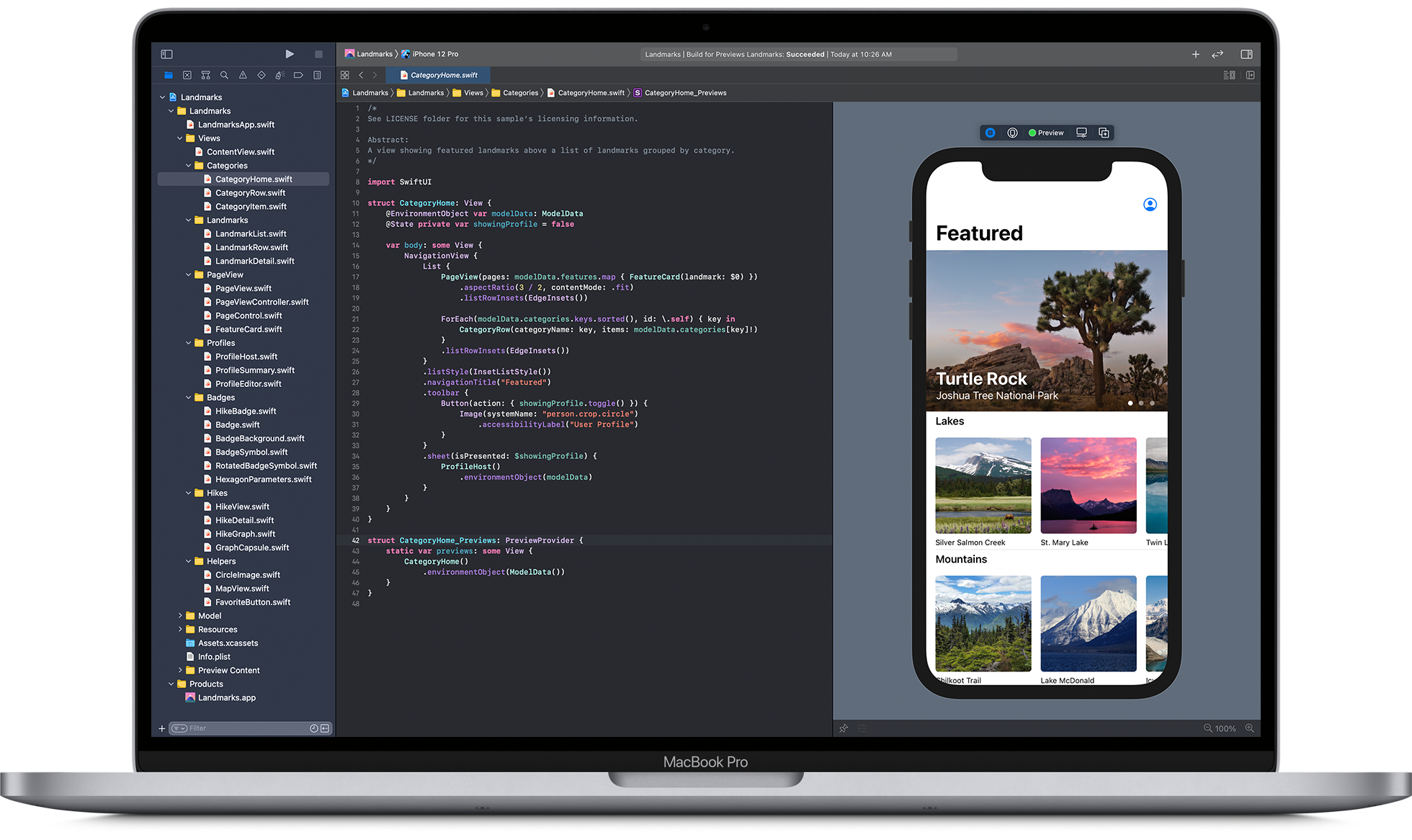
Debugging is the process of finding and fixing problems in a computer program. You can do debugging with a variety of different tools, but the most common are source code analysis tools, such as debuggers or profilers.
Building your app is the process of creating all of the files and modules that make up your application. This includes writing source code, creating documentation, and setting up build scripts.
Conclusion
In this final article in our series on app development, we’re going to take a look at how to debug and build your app. Debugging is essential for finding and fixing errors in your code, while building ensures that your application is runnable and meets all the required specifications. In this article, we’ll cover both of these topics in depth, so be sure to read through it before moving on to the next stage of app development.