Under its new Cloud-based Cloud brand, Google Cloud is expanding its reach into customers’ data cecentersnd out to the edge. It primarily targets customers with unique data ownership, latency, or local information requirements.
Google Distributed Datacenter Edge and Google Distributed Datacenter Hosted are the two new possibilities announcement was made this week. Both are supported by the Anthos product of Google Cloud, which enables customers to implement and maintain Kubernetes workloads in various environments.
“Google Distributed Data center is a selection of fully-managed operating systems that extends our functionality into customer data centers,” said Sachin Gupta, Google Cloud’s vice president and general manager of open infrastructure, during a media briefing last week.
The hardware will be supplied by a group of launch partners, including Cisco, Dell, HPE, and NetApp, as well as the software is based on the free Kubernetes tool Kubernetes, which Google developed in 2014
Together, these enhancements bring Google Cloud closer to its competitors, AWS and Azure, providing customers with more options for how and where to run and manage virtual servers.
“The move is a strong shot across the neck of both Microsoft’s Azure Arc and AWS Outposts,” CCS Insight analyst Nick McQuire told InfoWorld via email.
How does Google Distributed Cloud Edge work?
Image Source: Link
One of the first is Cloud Based Edge. It either enables customers to track application forms across Google’s 140+ global endpoints, partnering telecoms’ operator climates, their own data center or data centers facility, but also edge locations including a factory floor, whereas leveraging Google’s diverse data processing and predictive analysis good approximation to where that information is produced and absorbed.
This is intended for applications that require low-latency just at the edge, have local computational requirements that the public cloud cannot meet, or for private sector 5G or LTE tasks.
Google’s extension of its skills to the edge aligns with a wider trend among virtual servers who want to enable clients to interact with a growing number of devices—from factory-floor sensors to various sensors on devices, a central hub for which workforces can be done manage consistently.
Isaac Sacolick wrote, “The unique benefit of cloud service edge computing is the process of expanding underlying cloud platform and services, especially for consumers by now heavily invested in a public cloud.” “Want architects and developers to leverage edge-deployed AWS, Azure, or Search engine Cloud services? They also contemplate 5G-enabled mobile applications requiring low-latency data processing and machine learning at telco endpoints.
Google has lagged behind its competitors in this area but has recently taken steps to close the gap. This included the release of Anthos for telecommunications, collaborations with AT&T, Nokia, and Ericsson on 5Communicating messages, and the Google Mobile Cloud.
Where is the Google Distributed Cloud Located?
Image Source: Link
The second option, Distributed Cloud Decided to host, is primarily designed for customers. They must function in a hybrid environment and have rigorous local regulations or especially sensitive workloads. It promises a method for modernizing on-premises deployments by providing access to Google Cloud computing via a set of coherent APIs, but without being positioned to Google Cloud.
Gupta explained that the control plane is the difference between this and starting to run Kubernetes Motor (GKE) on with Anthos. When clusters are “on-premises or attended, it is the same Kubernetes, but with a controller plane [provided by Anthos],” he said. Therefore, Dispersed Virtualization relies on a full controller plane.
Google Cloud will print the future system to use a secure repository where the client can scan and validate them before transporting them across the air gap and applying them to their surrounding ecology.
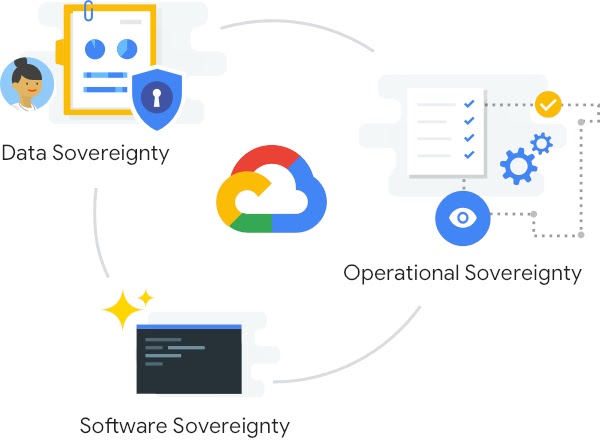
This builds upon an announcement Cloud Computing made last year regarding its commitments to data independence. “At Google people discuss the issues seriously, which are most often considered as term digital sovereignty. We are diligently working in three key areas:
- Data sovereignty,
- Operations and maintain independence, and
- Software sovereignty, to address the issue of digital sovereignty in the context of cloud computing.
Thomas Kurian even mentioned that “they focus on the feedback provided by the customers as well as policymakers and combine together to achieve excellent results.
GDC Edge Rack-based Configuration
Image Source: Link
This configuration is intended for telecom operators and telecom providers (CSP) to operate 5G core and airwaves access networks (RAN). CSPs can reveal the same facilities to their end users for running workloads requiring ultra-low latency, such as AI inference.
A Cloud-Based Edge Zone designates the location where rack-based hardware operates. Each zone operates on Google-provided, deployed, operated, and maintained hardware. Six servers and two lids (ToR) switches to connect the servers to a local network. Regarding storage, every physical server includes 4TiB discs. The weight capacity of an average rack is 900 pounds or 408kilogramss. The Cloud-Based Edge shelf arrives with the hardware, connection, and Cloud-Based settings specified during the ordering process.
Key Concepts in Distributed Computing on Google Cloud
PlatformGoogle Cloud Platform (GCP) provides a wide range of distributed computing capabilities for developers and businesses. Key concepts associated with GCP include scalability, availability, reliability, redundancy, data distribution, fault tolerance, and elasticity. Scalability allows users to increase or decrease the number of resources assigned to their applications as needed.
Availability ensures that components are available when they are required. Reliability guarantees that services will continue to perform even in the event of disruptions or outages. Redundancy ensures alternative paths exist for systems running with multiple layers of hardware or software redundancy. This provides higher levels of resilience against system failures. Data distribution enables fast processing by leveraging geographically dispersed servers. Therefore, This improves responsiveness and reducing latency when accessing files from anywhere in the world.
Fault tolerance is key in any distributed system where parts can fail. However, the overall system remains operational. This allows customers to stay connected without interruption, no matter what happens internally within a service provider’s environment. Lastly, elasticity makes sure resources scale up quickly based on customer demand and then scale down automatically during periods of low activity. This helps keep costs low and utilization high. It ensures customer performance needs remain satisfied at all times regardless of changes in workloads.
Google Cloud Products and Services for Distributed Computing
Google Cloud offers a comprehensive range of products and services for distributed computing, machine learning, and analytics. With options such as Google Compute Engine (GCE), Kubernetes Engine (Kubernetes) to build highly scalable applications or clusters, Bigtable to manage large datasets, CloudML for deep learning models development, and many others.
Using GCE enables organizations to launch virtual machines (VMs) on the cloud in seconds using its automated service. This supports Windows Server standard operating system along with other popular Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and CentOS. Google Kubernetes uses containers to make sure that apps run across multiple nodes without any manual intervention from your IT team. This scales up when you need more capacity and quickly rolling back if something goes wrong. It’s an ideal tool for running microservices-based apps like data processing pipelines or mission-critical applications like web servers. Bigtable makes it easy to store all kinds of large datasets so that they can be accessed in milliseconds. Moreover, it stores complex ones involving graphs or geospatial data.
And finally, CloudML helps businesses use massive amounts of data recorded by individuals through various connected devices. It allows them to develop advanced predictive models autonomously at scale without requiring custom code or special programming.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) on Google Cloud
Platform provides access to the powerful compute resources and storage necessary to drive innovation. With Google Cloud’s portfolio of services, users are able to develop, debug, run simulations and ultimately gain insights faster than ever before. Google Cloud HPC incorporates technologies such as GPUs, Persistent Memory (PMEM) for high-throughput storage solutions. It enables data-driven workloads on demand at scale and across both hybrid cloud platforms. It runs applications quickly with fully managed service on Kubernetes clusters. Moreover, it leverages multiple virtual CPUs per core to speed up compute processes. Additionally, its accelerated computing capabilities provide high-performance performance. It does by enabling distributed computation across multiple cores processors for faster results in fewer machines with less power consumption.
Conclusion
In today’s world, distributed computing on the Google Cloud Platform provides a great way to bring together multiple computers and servers in order to speed up your applications. By providing highly available infrastructure, containerized workloads, and other advanced features such as application scaling, distributed computing can be leveraged to provide much needed resources for almost any type of application. In addition to being tailored for scalability and flexibility, Google Cloud Platform offers various tools. This makes it easier for developers to create powerful applications quickly. From data analytics services like BigQuery and Machine Learning APIs like TensorFlow to serverless functions with App Engine and Kubernetes engine clusters – there is something for everyone when dealing with cloud-based solutions provided by the Google Cloud Platform.
FAQs
1. What is distributed computing on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP)?
Distributed computing on the Google Cloud Platform refers to the practice of processing large datasets or complex computational tasks across multiple interconnected computing resources within the GCP infrastructure.
2. What are the benefits of distributed computing on GCP?
The benefits of distributed computing on GCP include scalability, high performance, fault tolerance, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to leverage advanced analytics and machine learning tools.
3. What tools and services does GCP offer for distributed computing?
GCP offers several tools and services for distributed computing, including Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for containerized workloads, Google Cloud Dataproc for Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark clusters, and Google Cloud Bigtable for NoSQL databases.
4. How does GCP ensure scalability and performance in distributed computing?
GCP leverages a highly scalable and distributed infrastructure, allowing users to dynamically scale computing resources up or down based on demand. Additionally, GCP’s global network infrastructure and high-performance computing capabilities ensure optimal performance for distributed computing workloads.
5. How does fault tolerance work in distributed computing on GCP?
GCP provides built-in fault tolerance mechanisms, such as automatic instance replacement and data replication across multiple zones and regions. This ensures that distributed computing workloads remain resilient to hardware failures and other disruptions.
6. How does GCP help manage the cost of distributed computing?
GCP offers flexible pricing options and cost management tools to help users optimize their spending on distributed computing resources. This includes features such as sustained use discounts, preemptible VMs, and budget alerts.
7. Can I integrate GCP’s distributed computing services with other GCP services?
Yes, GCP’s distributed computing services can be seamlessly integrated with other GCP services, such as Google Cloud Storage for data storage, Google Cloud Pub/Sub for event-driven computing, and Google Cloud AI Platform for machine learning workloads.
8. What types of distributed computing workloads are suitable for GCP?
GCP can handle a wide range of distributed computing workloads, including data processing and analysis, machine learning and artificial intelligence, batch processing, real-time streaming, and high-performance computing (HPC).
9. How can I get started with distributed computing on GCP?
To get started with distributed computing on GCP, you can explore GCP’s documentation, tutorials, and sample projects. Additionally, you can leverage GCP’s free trial and credits to experiment with distributed computing workloads at no cost.
10. Are there any best practices for distributed computing on GCP?
Yes, there are several best practices for distributed computing on GCP, including optimizing resource utilization, designing fault-tolerant architectures, leveraging managed services, monitoring performance and costs, and following security and compliance guidelines. GCP’s documentation and support resources provide guidance on implementing these best practices.