A SAN is a high-performance network devoted to centralized block-level storage. Storage devices, toggles, as well as hosts are all linked together by the network. High-end corporate SANs might include SAN directors for improved performance as well as capacity utilisation.
Host bus adapters are used to connect servers to the SAN fabric (HBAs). The SAN is recognised by servers as domestically attached storage, allowing multiple servers to share a storage pool. SANs are not reliant on the LAN and help ease network congestion by offloading information directly from connected servers.
What are the methods of SAN?
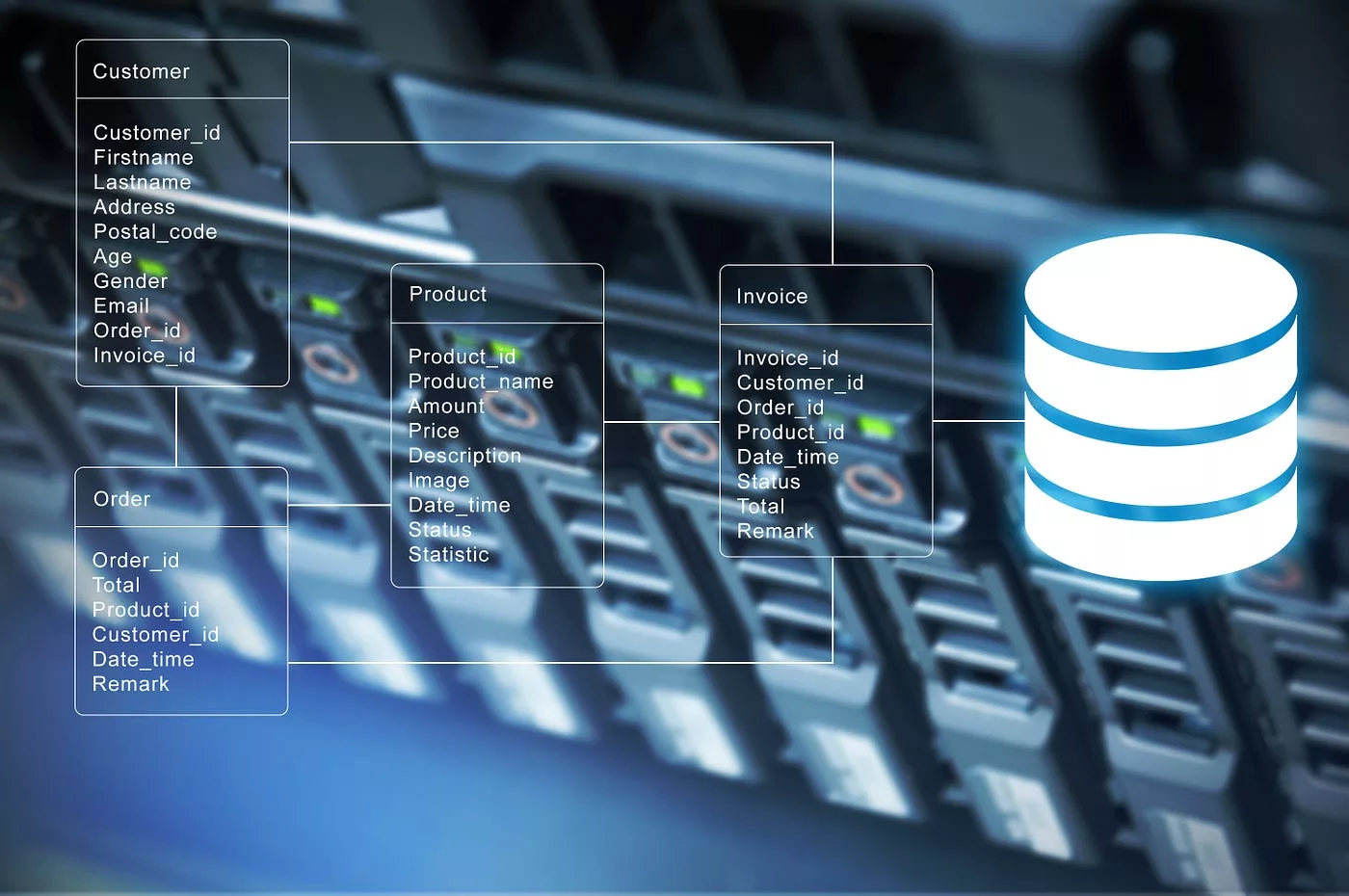
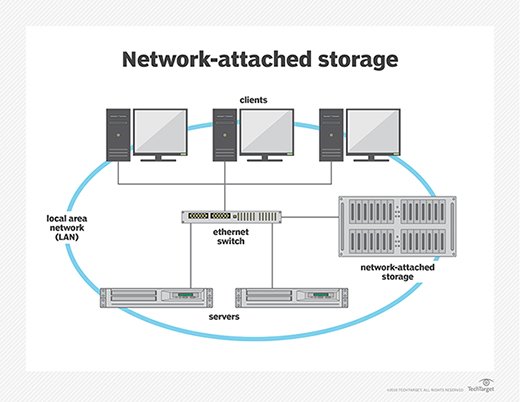
A storage area network (SAN) is a method of providing users with shared access to centralised, block level information storage, even enables various clients to access things at the same time with really superior efficiency. A SAN improves storage device availability by making disc arrays as well as tape libraries appear to customers as if they were exterior hard drives on their local network. A SAN provides the fastest access speed obtainable for media and mission critical saved information by creating a separate storage-based system for block accessing data over high-speed Fibre Channel as well as avoiding the constraints of TCP/IP protocols as well as local area network overcrowding.
SAN is generally used by huge companies and requires management by an IT staff because it is significantly more complicated and costly than NAS. Its high speed as well as low latency make it ideal for some applications, including such video editing. Video editing necessitates equitable and prioritised bandwidth utilisation from across the network, which is a benefit of SAN.
The negotiation of access permissions over Ethernet, combined with the serving of files via extremely fast Fibre Channel, results in very responsive performance on network computers, even with very large datasets. Consequently, SAN has become widely used in collaborative video editing environments.
SAN Varieties
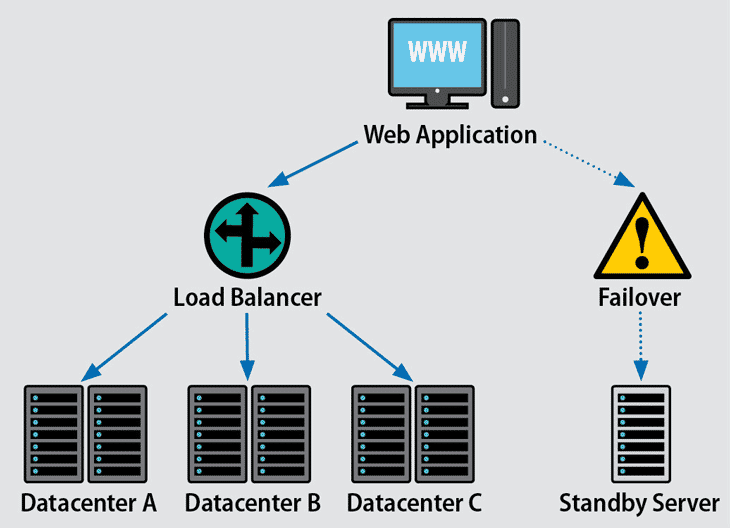
Image Source: Link
The following are the most common SAN protocols:
Protocol for Fibre Channel (FCP)-
The most widely used SAN or block protocol, accounting for 70% to 80% of the overall SAN market. FCP employs Fibre Channel transport protocols, which include embedded SCSI instructions.
Small Computer System Interface for the Internet (iSCSI)
The very next largest SAN or block protocol, accounting for approximately 10% to 15% of the economy. iSCSI encapsulates SCSI commands within an Ethernet frame and afterwards transports them over an IP Ethernet network.
Ethernet over Fibre Channel (FCoE)
FCoE accounts for less than 5% of the SAN market. Because it encompasses an FC frame inside of an Ethernet datagram, it is similar to iSCSI. Then, similar to iSCSI, it transports data over an IP Ethernet network.
Fibre Channel Nonvolatile Memory Express (FC-NVMe)
NVMe, an interface protocol based on the PCI Express (PCIe) bus, delivers flash storage and supports hundreds or thousands of concurrent queues, unlike traditional all-flash architectures with a single serial command queue, allowing for simultaneous processing of commands.
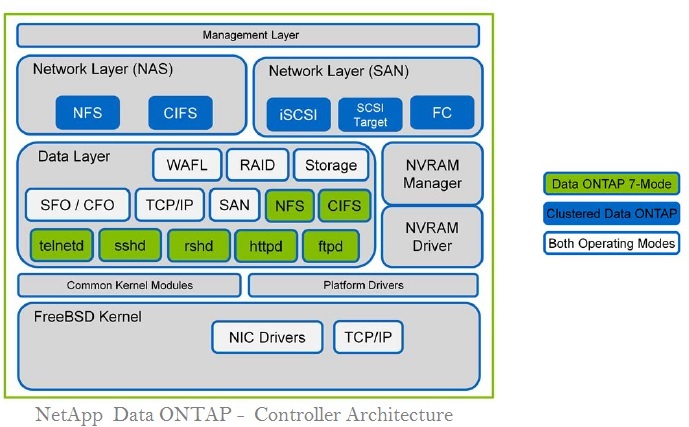
What exactly is unified storage?

Image Source: Link
Unified storage, also known as multiprotocol storage, arose from the desire to eliminate the need to purchase SAN and NAS as separate storage platforms and instead combine unified block and file storage in a single system. A single system can support Fibre Channel and iSCSI block storage, as well as file protocols like NFS and SMB, with unified storage. NetApp receives wide credit for inventing unified storage, although numerous vendors now offer multiprotocol options.
According to Sinclair, the majority of midrange corporate storage arrays today are multiprotocol. Instead of purchasing a SAN storage box as well as a NAS storage box, you can purchase a single box that supports all four protocols.
Is SAN storage a viable backup solution?
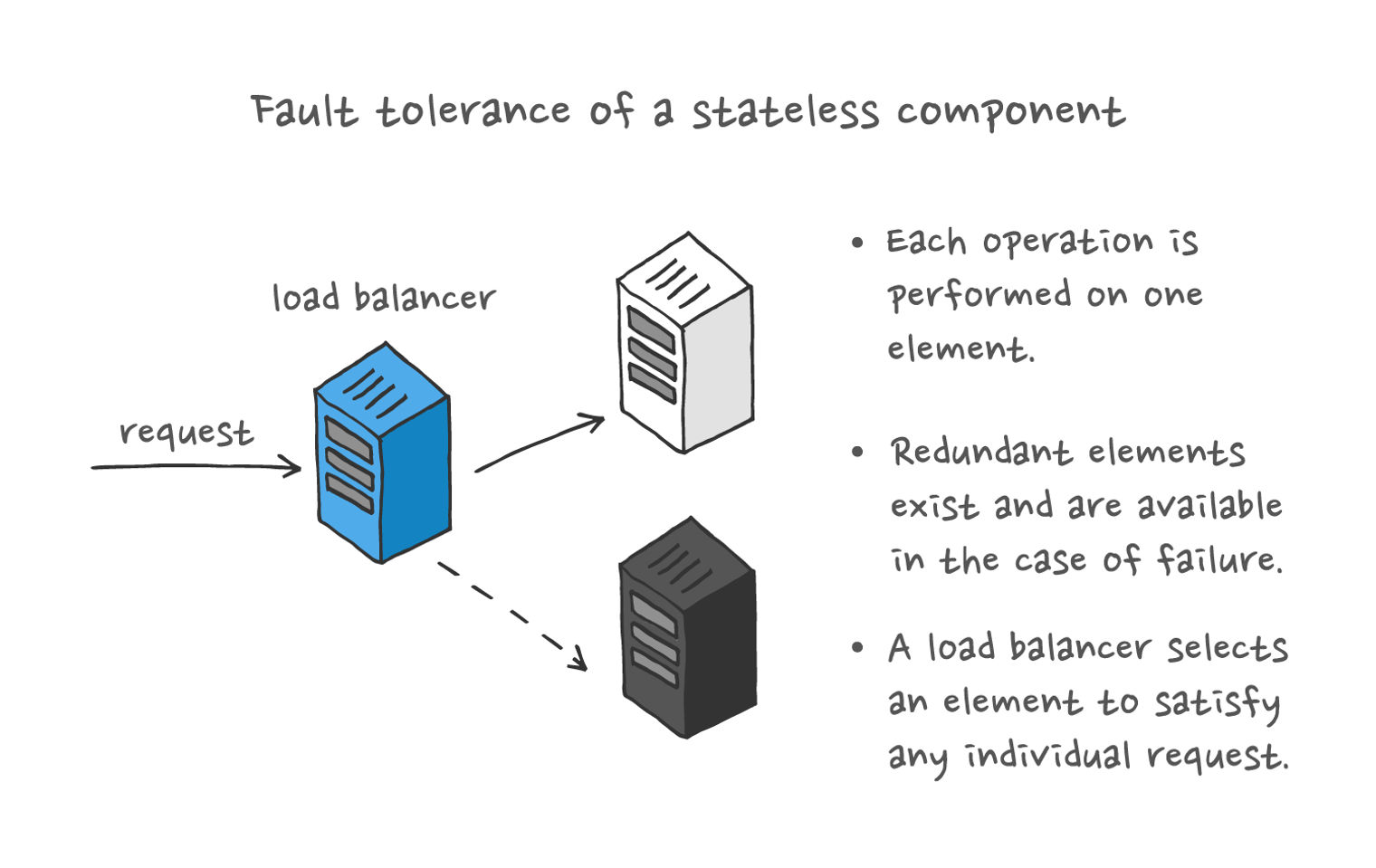
Image Source: Link
Storage area networks are ideal for backup for several reasons:
SANs allow you to consolidate backups from different servers into a single location and scale up storage space as needed.
A SAN solution also allows for faster backup systems. Servers can back up directly to the SAN without traversing the LAN, avoiding impacts from local network traffic on the backups.
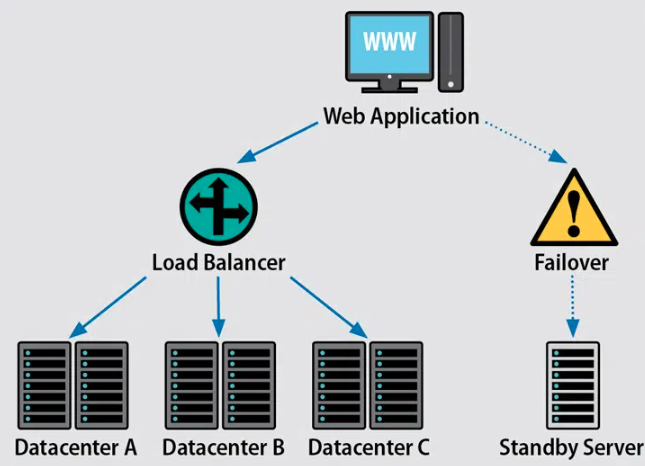
When one of the servers in a SAN cluster fails, the volume of work from such a server will instantly failover to another server in the SAN. Data can also be reproduced to an offsite SAN to aid in disaster response.
A SAN, built on a network fabric connecting storage devices and computers, can activate an alternate path if one network route fails. This reduces the possibility of a single device failure rendering storage inaccessible.
FAQs
What is SAN (Storage Area Network) reliability and fault tolerance?
SAN reliability and fault tolerance refer to the system’s ability to maintain data availability and integrity despite hardware failures or errors.
How does SAN ensure reliability?
SAN achieves reliability through redundant components such as RAID arrays, dual controllers, and hot-swappable drives, minimizing the risk of data loss.
What is fault tolerance in SAN?
Fault tolerance in SAN refers to the system’s ability to continue operating without interruption in the event of hardware failures or errors.
How does SAN handle disk failures?
SAN employs RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) technology to mitigate disk failures by distributing data across multiple disks and providing redundancy.
Can SAN recover from component failures?
Yes, SAN can recover from component failures by using redundant components and failover mechanisms that automatically switch to backup components.
How do I ensure high availability in SAN?
Ensure high availability in SAN by implementing redundant paths, dual controllers, and failover mechanisms to minimize downtime and data loss.
Is SAN fault tolerance scalable?
Yes, SAN fault tolerance is scalable through technologies like clustering and virtualization, allowing for seamless expansion and maintenance without impacting reliability.