Are you looking for a secure and scalable storage solution that can handle your data growth? Look no further than AWS Simple Storage Service (S3)! With its flexible object-based architecture, S3 provides an easy-to-use platform for storing and retrieving any amount of data from anywhere in the world. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, S3 offers the perfect blend of durability, availability, security, and performance to meet your business needs. So let’s dive into the fundamentals of AWS S3 and discover how it can help take your organization to new heights!
Understanding Object Storage in AWS S3
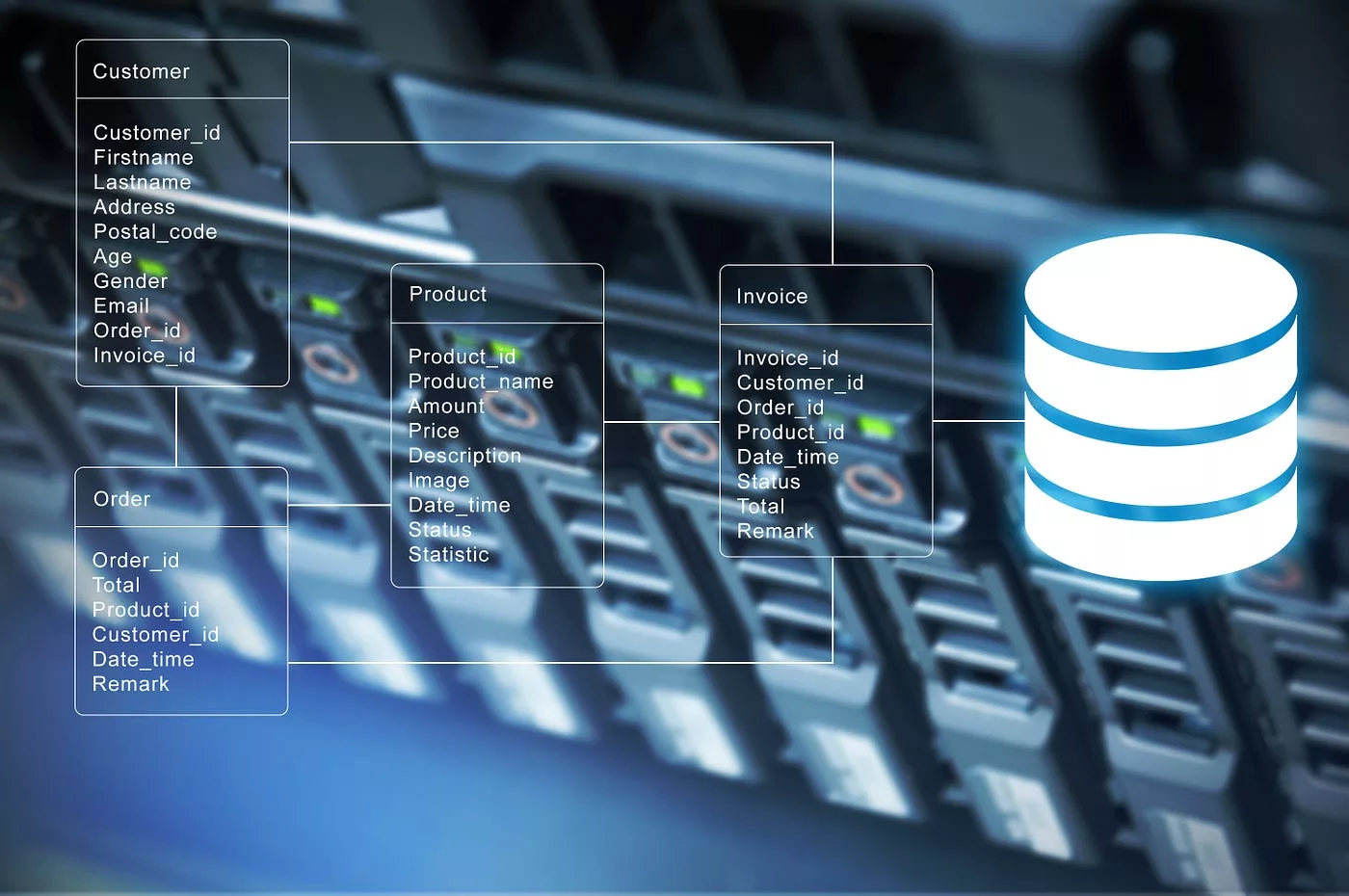
Object storage is a type of data storage that stores data in discrete units called objects. In AWS S3, these objects can be anything from documents to images and videos. Each object has its own unique identifier and metadata that describes the contents of the object. Understanding how object storage works in AWS S3 is crucial for the efficient management of your data.
Managing S3 Buckets
When it comes to managing S3 buckets, there are a few things you need to keep in mind. There are certain limitations and naming conventions that you should be aware of when creating S3 buckets. Additionally, there are size limitations for objects as well as options for versioning. It’s also important to understand how to manage object metadata and access control using AWS S3 tags. Proper management of your S3 buckets is crucial for efficient data storage and organization.
Creating S3 Buckets: Limitations and Naming Convention
When creating S3 buckets, there are certain limitations and naming conventions that need to be followed. Bucket names must be unique globally and should only contain lowercase letters, numbers, hyphens, and periods. They cannot start or end with a period or have consecutive periods in their name. Additionally, bucket creation is subject to default service quotas that limit the number of buckets per account. Keep these limitations in mind when setting up your AWS S3 storage environment for smooth operation.
S3 Object Size Limitations and Versioning
AWS S3 imposes certain size limitations on objects to be stored in the buckets. The maximum object size is 5 terabytes, which is more than sufficient for most use cases. Additionally, AWS S3 versioning allows you to keep multiple versions of an object within a single bucket, providing additional protection against accidental deletion or modification of data. This means that your data remains secure and protected at all times, giving you peace of mind when it comes to storing important files.
Managing S3 Object Metadata and Access Control
One important aspect of AWS S3 is managing object metadata and access control. With S3, you can add custom metadata to your objects for efficient organization and retrieval. Additionally, you have full control over who can access your data with flexible bucket policies and access controls. This ensures that only authorized users can view or modify the data stored in your S3 buckets.
Using AWS S3 Tags for Efficient Data Management
AWS S3 tags provide a simple yet powerful way to categorize and organize your data. By applying tags to your objects, you can easily search for and filter data based on specific criteria such as business unit, project name or cost center. This helps you keep track of who created the object when it was created and what its purpose is. With AWS S3 tags, managing your data becomes more efficient and streamlined than ever before.
AWS S3 Regions and Static Websites
AWS S3 is a globally distributed service with multiple regions and availability zones. Each region consists of several availability zones that are geographically separated data centers, providing high availability for your data. You can host static websites on AWS S3 by configuring the bucket as a static website hosting endpoint. Moreover, you can choose the region in which to store your data and configure it to replicate across different regions for better durability and low-latency access.
Securing S3 Data Access
When it comes to securing S3 data access, AWS offers a variety of options. One such option is data encryption, which ensures that your data is protected both in transit and at rest. Additionally, bucket policies can help control who has access to your S3 buckets and what actions they’re allowed to take. These measures not only keep your data safe but also give you peace of mind knowing that the information stored on AWS S3 is secure.
Data Encryption in AWS S3
Data encryption in AWS S3 is a crucial part of securing your data. AWS provides various options for encrypting data at rest, including server-side and client-side encryption. Server-side encryption offers the option to use Amazon S3-managed keys or customer-provided keys, while client-side encryption allows you to manage your own keys outside of AWS. Additionally, using HTTPS when accessing your S3 buckets over the internet helps protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Lifecycle Management, Bucket Policy, and Data Protection
One key feature of AWS S3 is its lifecycle management capability. This allows you to define rules for transitioning objects to different storage classes or deleting them all together based on their age or other criteria. Additionally, bucket policies can be used to control access and permissions at the bucket level, while data protection measures such as versioning and encryption help ensure the integrity of your stored data.
Understanding AWS S3 Storage Classes
AWS S3 offers different storage classes with varying levels of durability, availability, and cost. The Standard class provides high performance but comes at a higher cost. Infrequent Access (IA) is suitable for data accessed less frequently while reducing costs. Glacier allows archiving of rarely accessed data at a much lower cost but takes longer retrieval times. There’s also the Intelligent Tiering that automates data movement among storage classes based on usage patterns to optimize costs without sacrificing performance or accessibility.
Featured Use Cases of AWS S3
AWS S3 is one of the most widely used object storage services in the world. Organizations across various industries have adopted it to store and manage their data efficiently. From hosting static websites to managing large-scale analytics workloads, AWS S3 provides a versatile platform for all your storage needs. Some popular use cases include backup and disaster recovery, video and image storage, data archiving, IoT device data management, content delivery networks (CDNs), big data analytics, and machine learning applications.
Conclusion
As you wrap up your journey exploring AWS Simple Storage Service (S3), keep in mind the numerous resources available to help you continue learning about this powerful storage solution. From online documentation and tutorials to community forums and AWS certifications, there are endless opportunities for growth and development. Keep pushing yourself to explore new use cases and best practices, and never hesitate to reach out for support along the way. Happy storing!
By now, you should have a good understanding of the fundamentals of AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) and how it can benefit your business. With its flexible storage options and powerful features, S3 is an essential tool for businesses that need reliable cloud-based storage solutions.
To continue learning about AWS S3 and other cloud technologies, be sure to sign up for updates from Amazon Web Services. You can also explore the various AWS certification programs available to deepen your knowledge and skills in this field.
Whether you are just getting started with cloud computing or looking to take your skills to the next level, AWS has resources and tools that can help you achieve your goals. So why wait? Start exploring today!