Welcome to the world of Big Data – where information reigns supreme and endless possibilities await! In this era of digital innovation, we generate an astonishing amount of data every single day. From social media interactions to online transactions, from sensor readings to medical records, our digital footprint is expanding at an exponential rate.
But what exactly is Big Data? Well, it’s not just about the sheer volume of data we’re dealing with. It goes beyond that. Big Data encompasses three key dimensions: velocity, variety, and veracity – commonly known as the Three V’s. These elements present challenges and opportunities for businesses and organizations seeking to harness the power of data-driven insights.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deeper into the world of Big Data by exploring its definition and understanding its benefits. We’ll also take a closer look at some cutting-edge storage and processing technologies. It has revolutionized how we manage and analyze massive datasets. So buckle up as we embark on this exciting journey through the realm of Big Data!
What is Big Data?
Big Data. It’s a term that has become increasingly popular in recent years, but what does it really mean? At its core, Big Data refers to the vast amount of information that is generated and collected from various sources at an unprecedented scale. We’re not just talking about gigabytes or terabytes here; we’re dealing with petabytes, exabytes, and beyond!
The Three V’s of Big Data – velocity, variety, and veracity – help us understand the unique characteristics of this data deluge. First off, velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed. With real-time interactions happening on social media platforms and streaming services delivering content instantly, the pace at which data flows can be mind-boggling.
Next up is variety. Unlike traditionally structured datasets stored neatly in rows and columns within databases, Big Data comes in various formats such as text documents, images, videos, and audio files – you name it! This diversity poses a challenge when it comes to organizing and extracting meaningful insights from these disparate sources.
Veracity emphasizes the importance of ensuring data accuracy and reliability. Given the sheer volume and heterogeneity of Big Data sources, there may be inherent uncertainties or inconsistencies within the dataset itself. Verifying its authenticity becomes crucial for making informed decisions based on this wealth of information.
To truly harness the power of Big Data requires advanced storage infrastructure capable of handling massive amounts of information efficiently while maintaining high availability. Additionally,
processing technologies like distributed computing frameworks enable parallel processing across multiple nodes or clusters to tackle complex analytical tasks effectively.
The Three V’s of Big Data
When it comes to understanding the concept of big data, it is crucial to grasp the three fundamental characteristics that define and differentiate it. These are commonly known as the three V’s of big data: volume, velocity, and variety.
Volume refers to the sheer amount of data generated every second by various sources such as social media platforms, sensors, devices, and more. This massive volume requires specialized storage systems capable of handling vast amounts of information efficiently.
Velocity emphasizes the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed in real-time or near-real-time. With technology advancements like IoT (Internet of Things) devices continuously streaming data and online transactions occurring at lightning-fast speeds, organizations must have robust processing capabilities to keep up with this relentless flow.
Variety highlights the diverse nature of today’s data sources. Traditional structured databases were designed for homogeneous datasets with a fixed schema structure. However, contemporary big data include unstructured or semi-structured formats like text documents, images, videos, audio files, and log files – making it essential for businesses to employ versatile technologies that can handle these varying types effectively.
Understanding these three V’s enables us not only to comprehend what constitutes big data but also underscores why traditional storage and processing approaches often fall short when faced with its challenges. In an era where collecting insights from vast amounts of complex information has become vital for decision-making processes across industries – embracing cutting-edge technologies tailored for big data becomes essential.
The Benefits of Big Data
Big Data has become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing how we collect, analyze, and utilize information. With the exponential growth of digital data, organizations are now able to derive valuable insights from vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. The benefits of harnessing Big Data are numerous and far-reaching.
One major advantage is improved decision-making. By analyzing large datasets in real time, companies can gain valuable insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency. This allows them to make informed decisions that drive business growth and stay ahead of their competitors.
Big Data also enables personalized experiences for customers. By leveraging customer data such as browsing history and purchase patterns, businesses can tailor their offerings to individual preferences. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also increases loyalty and retention rates.
Another benefit is enhanced fraud detection capabilities. Through advanced analytics techniques applied to Big Data sets, organizations can identify potential fraudulent activities in real-time or even predict them before they occur. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and protect both businesses and consumers.
Moreover, Big Data plays a crucial role in healthcare advancements. By analyzing patient records, genetic information, clinical trials data, and other relevant sources on a large scale using machine learning algorithms or artificial intelligence models – medical professionals are empowered with valuable insights that lead to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatments.
In addition to these advantages mentioned above – which barely scratch the surface – Big Data presents opportunities for innovation across various industries such as transportation (e.g., optimizing routes based on traffic patterns), manufacturing (e.g., predictive maintenance), finance (e.g., risk management), marketing (e.g., targeted advertising campaigns), to name a few.
Big Data Storage and Processing Technologies
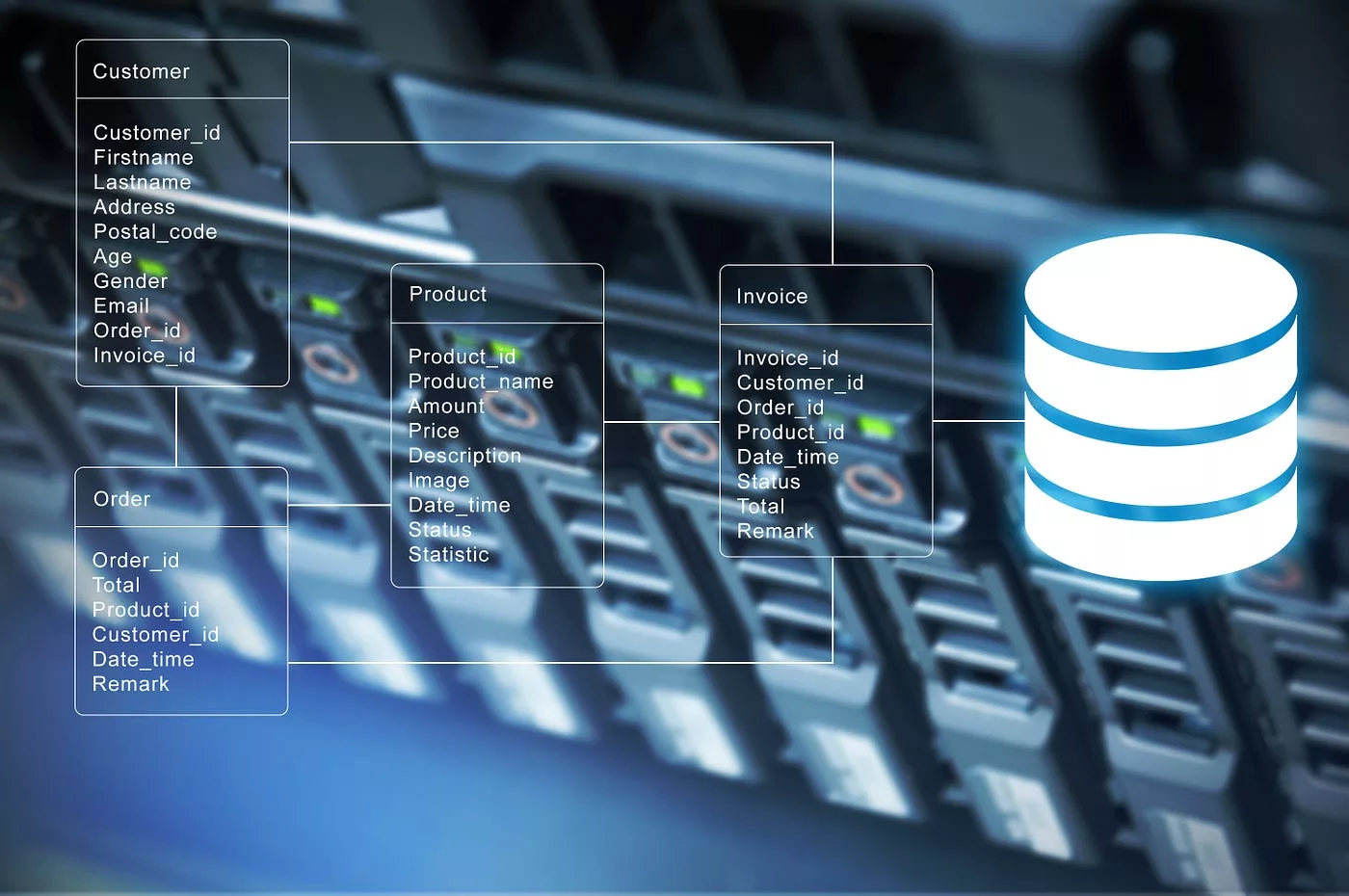
When it comes to dealing with the massive amounts of data generated in today’s digital age. It has efficient storage and processing technologies is essential. Big data refers to the vast volumes of structured and unstructured information organizations gather from various sources.
To effectively handle big data, storage solutions need to be scalable, flexible, and reliable. Traditional relational databases may not be sufficient for storing and analyzing large datasets. Instead, organizations are turning to innovative technologies such as distributed file systems like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) or object storage like Amazon S3.
These technologies allow businesses to store huge amounts of data across multiple servers or cloud-based platforms. By distributing the workload across a cluster of machines, these systems can handle high-speed input/output operations efficiently.
In terms of processing big data, parallel computing frameworks like Apache Spark have gained popularity due to their ability to process data in memory rapidly. This allows for real-time analytics and faster decision-making.
What’s more in store for you?
Other technologies used for big data processing include Apache Kafka for stream processing, NoSQL databases like MongoDB for handling unstructured information, and graph databases like Neo4j for managing complex relationships within the dataset.
By leveraging these advanced storage and processing technologies, organizations can unlock valuable insights from their big data sets. They can gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior patterns and optimize business processes. Moreover, they can also detect fraud or anomalies in real-time transactions, and personalize marketing campaigns based on individual preferences.
The field of big data continues to evolve rapidly as new tools and techniques emerge. As technology advances further with innovations such as machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence models integrated into big-data platforms – we can only imagine the endless possibilities that lie ahead!
An exciting time awaits us as we continue exploring the potential benefits that come with enhanced big-data storage capabilities coupled with powerful processing technologies! So stay tuned!
Conclusion
In today’s data-driven world, Big Data has become an integral part of businesses across various industries. With the exponential growth in the volume, velocity, and variety of data, organizations are constantly seeking efficient storage and processing technologies to harness the power of Big Data.
Throughout this article, we have explored what Big Data is and how it is characterized by the three V’s – volume, velocity, and variety. We have also discussed the numerous benefits that Big Data offers to businesses. This includes improved decision-making capabilities, enhanced customer experiences, increased operational efficiency, and competitive advantage.
When it comes to storing and processing Big Data effectively, there are several technologies available in the market today. Traditional relational databases may not be suitable for handling large-scale datasets. Instead, organizations can turn to distributed file systems like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) or cloud-based storage solutions such as Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage.
For processing massive amounts of data quickly and efficiently, technologies like Apache Spark offer high-speed in-memory analytics capabilities. Streaming platforms like Apache Kafka enable real-time data ingestion and processing for applications. This requires immediate insights from rapidly changing datasets.