This study compares and contrasts the cloud services offered by Cloudera, Amazon, and Microsoft Azure. Big data refers to vast volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information. Conventional technologies are incapable of storing and processing big data, and the Hadoop framework allows for storing and processing such complicated data. Cloudera, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure have installed Hadoop and enabled cloud-based data storage and processing. Each distribution offers cloud computing, data storage, databases, and machine learning. They each possess unique strengths and weaknesses in different areas. Cloud service users must select the distribution as best meets their needs.
Description (Brief background)
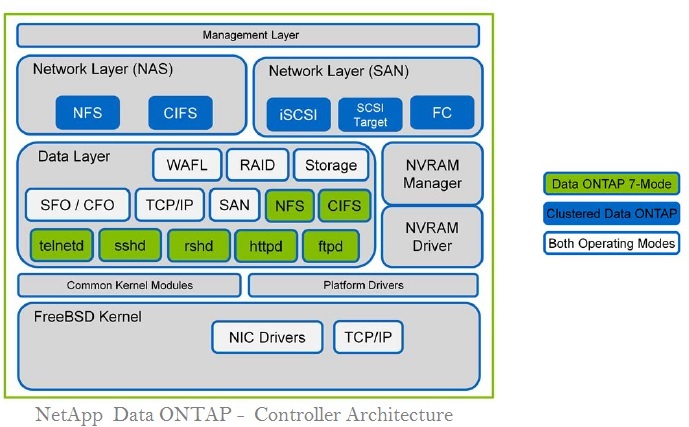
Cloudera Hortonworks Big data is a word that refers to voluminous (volume), rapidly expanding (velocity), and diverse databases (variety). Conventional technology and tools, such as Database Management System (RDBMS), are neither enough nor suitable for managing, capturing, processing, or analyzing massive data to provide significant insights.
Two other definitions of big data Cloud service include truth and value.
Volume:
Data relating to the size of the data. Data volume has escalated from megabytes to gigabytes, with vast amounts of data generated every second. Forecasts predict that by 2020, we will have created 40 zettabytes of information, which is 300 times more than what was created in 2005.
Cloudera Hortonworks RDBMS is only ideal for structured data kept in a table format, whereas big data includes a wide variety of data types in addition to tables. Big data consisted of unstructured data such as information generated by mobile devices, photos, and videos. In RDMBS, it analyzes the data depending on the relationships, which results in a further constraint because it cannot preserve unstructured data relationships (yet). Aside from this, RDBMS does not promise quick processing speed, which is one of the primary concerns when evaluating large amounts of data. With NoSQL and a distributed file system, big data analytics consequently enhances. Conventional technologies and techniques will be costly for storing and processing massive data sets.
Variety refers to the numerous forms of Cloudera Hortonworks data and data sources. Big data extends beyond the rows and columns of structured data found in a data warehouse, which represents only a small portion of big data. The amount of the information generated is unstructured or semi-structured, such as music, movies, photos, email, and social networking data. Daily, 400 million tweets are being sent to Twitter’s 200 million active users. All of these factors contribute to the expanding diversity of big data.
Velocity:
Speed refers to the rate at which data produces and processes. Some data are static and do not change, as well as data that change regularly. For often changing or rapidly created data, such as posts on social media, the processing speed must be sufficient, as the data may become obsolete over time.
Cloudera Hortonworks Validity relates to the dependability or inaccuracy of data. Discrepancy and incompleteness in data collection contribute to data uncertainty.
The benefit that may be derived from data defines its value. The big data ecology demonstrates that big data and consumers can derive value from the data gathered and integrated by others along the data value stream.
Origins and Development of Distributions / Services
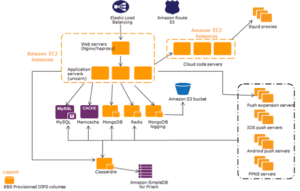
When standard technology and techniques prove inadequate for storing and processing massive amounts of data, developers introduce alternative distributions and services. Most distributions support the Hadoop framework, which can manage complicated and huge data sets.
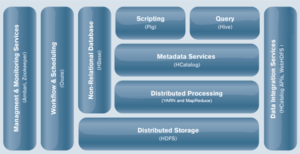
The Apache Foundation developed Hadoop (Highly Compressed Distributed Item Computing), an open-source software framework, in Java to facilitate the distributed parallel computation of massive data sets among clusters of commodity hardware using simple programming methods. The creator named it after his son’s stuffed elephant. In 2005, two Yahoo workers built Hadoop to support an open-source web crawler called Nutch. In 2003, Google launched Google File System & Google Map Reduce; then, in 2004, Google published white papers explaining Google File System and MapReduce. Google inspired the development of Hadoop. In 2005, Hadoop started to serve in Yahoo. In 2008, Apache acquired Hadoop, so Hadoop is now referred to as Apache Hadoop. Hadoop is now one of distributed systems’ most effective data storage and processing frameworks.
Conclusion
Hadoop allows storing, accessing, and obtaining vast resources of big data in a distributed manner with little cost, great scalability, and high availability, as it can identify failure at the application level, making it fault-tolerant. It can manage massive volumes of data and a wide variety of data types, including photos, videos, audio files, files, folders, software, and email. Hadoop can effectively manage organized, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Cloudera, Hortonworks, and MapR are Hadoop distributions with commercial support.