Cloud computing is slowly but steadily becoming the de facto standard for data-driven commercial operations. It’s no surprise, given how much value the cloud provides. It’s utilized for various activities, including streamlining workflows, scaling applications efficiently, managing algorithms and neural networks, etc.
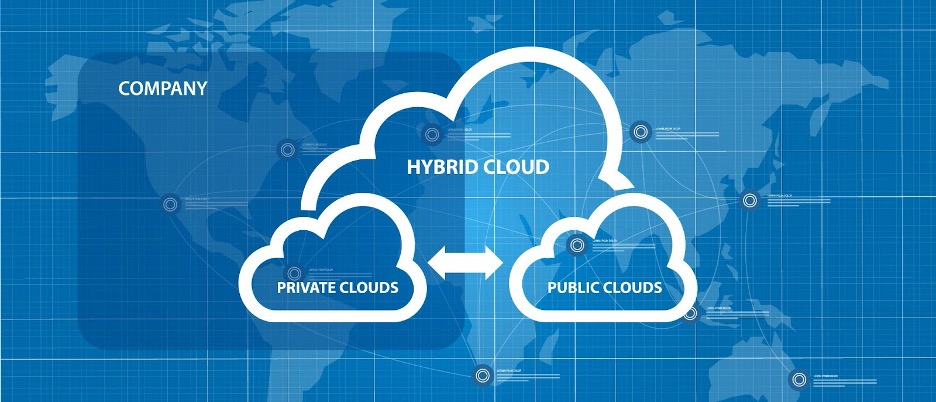
However, these are well-known facts. What’s less well known is that there are multiple different sorts of cloud platforms, each tailored to specific functions. Solutions for the public, corporate, and hybrid clouds are available.
What exactly is a public cloud?
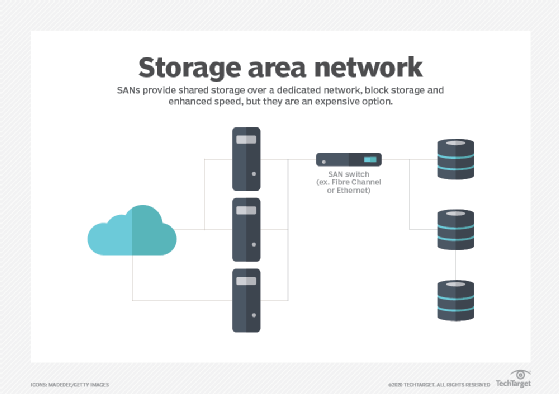
Image Source: Link
The phrase “public cloud” refers to a broad definition of a cloud platform. It is also the most widely used type of cloud computing by businesses of all sizes. Your organization referred to as a “cloud tenant,” shares equipment, storage, and internet infrastructure with other businesses.
A third-party vendor owns and manages the cloud resources (hardware, software, and related infrastructure) (like cloud services from Google, Microsoft Azure, AWS, and IBM). The services are offered over the internet and are controlled through a web browser. The cost-effectiveness of a cloud platform is its distinguishing attribute. You receive a great deal on scalability and flexibility of computer capacities and comparatively affordable service prices.
The phrase “public cloud” refers to a broad definition of a cloud platform. It is also the most widely used type of cloud computing by businesses of all sizes. Your organization referred to as a “cloud tenant,” shares equipment, storage, and internet infrastructure with other businesses. A third-party vendor owns and manages the cloud resources (hardware, software, and supporting equipment) (like cloud services from Google, Microsoft Azure, AWS, and IBM). The services are offered over the internet and are controlled through a web browser. The cost-effectiveness of a cloud platform is its distinguishing attribute. You receive a great deal on scalability and flexibility of computer capacities and comparatively affordable service prices.
Predictable computing requirements applications (tools available for communications and analytics, etc.)
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Using the Public Cloud
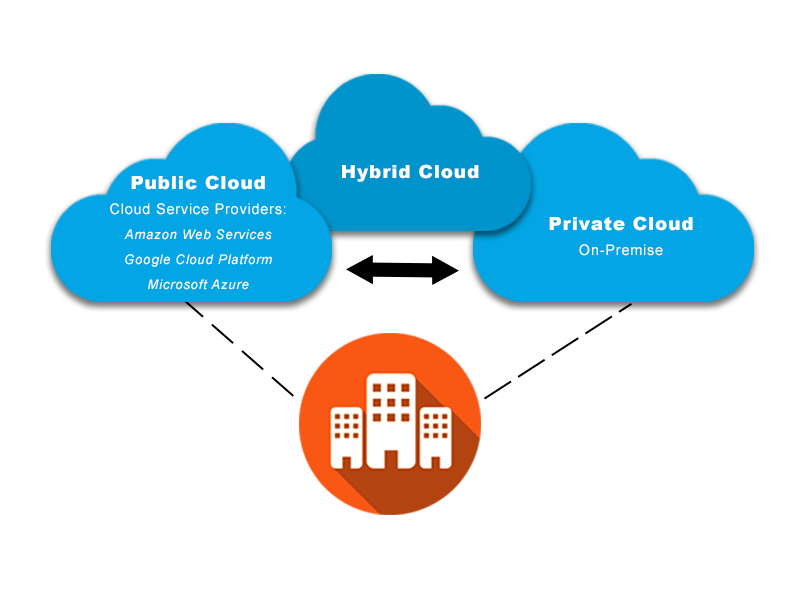
Image Source: Link
The following are some of the benefits of using a public cloud solution:
- Fully automated Deployment. There is no need to invest in infrastructure. The infrastructure is deployed and maintained by the cloud service provider.
- Superior workload scalability and dependability. Autoscaling features in public cloud architecture help you balance your workload and avoid outages and crashes.
- Low overall cost – the pricing scheme is flexible, covering just the used resources.
- The lower service costs are related to a variable pricing approach that only covers used resources.
- The flexibility of cloud infrastructure platform solutions may cover many corporate demands, from storage to complex predictive analytics machine learning.
The following are some of the public cloud’s drawbacks:
As a company’s cloud infrastructure grows, the overall cost rises dramatically. Privacy is always a serious topic for the cloud platform due to its nature. While you can help, there’s no assurance that the cloud hosting will be updated. Infrastructure oversight is limited, leading to problems complying with various requirements.
What is a Private Cloud, and how does it work?
Image Source: Link
A private cloud is a type of cloud computing where the infrastructure is built and used solely by one company. This type of cloud service can even be installed in the firm’s data center (or managed by a third party).
The key distinction between public and private clouds is the company’s much greater control over the system. The company maintains the equipment and infrastructure. No one outside can use the system resources since they are separated into a secure and private network.
The key benefits of using a private cloud are control and security. As a result, it is ideal for government agencies, legal and financial organizations, and large corporations – in short, any business that requires a rapid turnaround of sensitive data.
The cloud infrastructure is never used as a singular cloud solution as it is now. The usage of the cloud infrastructure in conjunction with the cloud platform as a location to hold sensitive data is becoming more widespread.
As a result, a private cloud is a viable choice for businesses that demand great adaptability and configuration flexibility. Going private cloud makes sense for firms with the financial resources to cover the price of running their on-premise cloud-based data center.
In the following scenarios, the cloud service is the better option in terms of operations:

Image Source: Link
Systems containing sensitive data require private hosting and strict security measures. For instance, when cloud ERP systems store individually identifiable information like social security numbers and addresses, application maintenance becomes predictable in terms of scalability and storage costs. Companies must host data and applications that are vital or sensitive to their operations when strict privacy, low latency, legal compliance, and high data protection levels are necessary.
Data Mobility and Seamless Resource Migration:
SAN enables data mobility and resource migration within cloud environments. With SAN, organizations can seamlessly move data and resources between different storage arrays or servers without interrupting operations. This flexibility allows for workload balancing, resource optimization, and data accessibility across the cloud infrastructure.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Solutions:
SAN plays a crucial role in backup and disaster recovery strategies for private and hybrid clouds. SAN solutions provide efficient data replication and snapshot capabilities, enabling organizations to create reliable backup copies of critical data and applications. In the event of a failure or data loss, SAN facilitates quick and efficient recovery, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Virtual Machine Storage Management:
SAN technology offers advanced storage management features for virtual machines (VMs) in private and hybrid cloud environments. By leveraging SAN, organizations can optimize VM storage allocation, ensure performance and availability, and simplify provisioning and management tasks. SAN provides granular control over VM storage resources, enabling efficient utilization and scaling.
Optimizing Performance and Workload Distribution:
SAN applications in cloud infrastructure optimize performance and workload distribution. SAN solutions leverage features such as load balancing, caching, and tiered storage to ensure optimal data access and performance. By distributing workloads across multiple storage devices and tiers, SAN minimizes bottlenecks and enhances overall system efficiency.
Security and Data Protection in SAN for Cloud:
Data security and protection are paramount in private and hybrid cloud environments. SAN offers robust security mechanisms, including access controls, encryption, and data integrity checks. SAN’s centralized storage architecture enables organizations to implement consistent security policies, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity across the cloud infrastructure.
Integration with Cloud Management Platforms:
SAN seamlessly integrates with cloud management platforms, providing centralized storage management and monitoring capabilities. SAN solutions offer APIs and integrations with popular cloud management platforms, allowing administrators to automate storage provisioning, monitor performance, and streamline resource allocation.
Cost Efficiency and ROI Considerations:
SAN applications in private and hybrid clouds contribute to cost efficiency and a positive return on investment (ROI). By leveraging SAN’s storage consolidation, organizations can reduce hardware and maintenance costs. SAN’s scalability and efficient resource utilization minimize wasted storage capacity, resulting in optimized cost management.
Use Cases and Benefits of SAN in Private and Hybrid Clouds:
SAN finds numerous use cases and benefits in private and hybrid cloud environments. Some common use cases include enterprise application hosting, database storage, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), big data analytics, and content delivery networks (CDNs). SAN offers benefits such as improved data performance, scalability, simplified management, data protection, and enhanced disaster recovery capabilities.
Choosing the Right SAN Solution for Cloud Infrastructure:
When selecting a SAN solution for private and hybrid cloud infrastructure, organizations must consider factors such as scalability, performance, compatibility with existing infrastructure, integration capabilities, support services, and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating these factors will help organizations choose a SAN solution that aligns with their specific cloud requirements and provides the necessary features for optimal storage management and data protection.
FAQs on SAN Applications in Private and Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure:
1. What is SAN (Storage Area Network) in the context of cloud infrastructure?
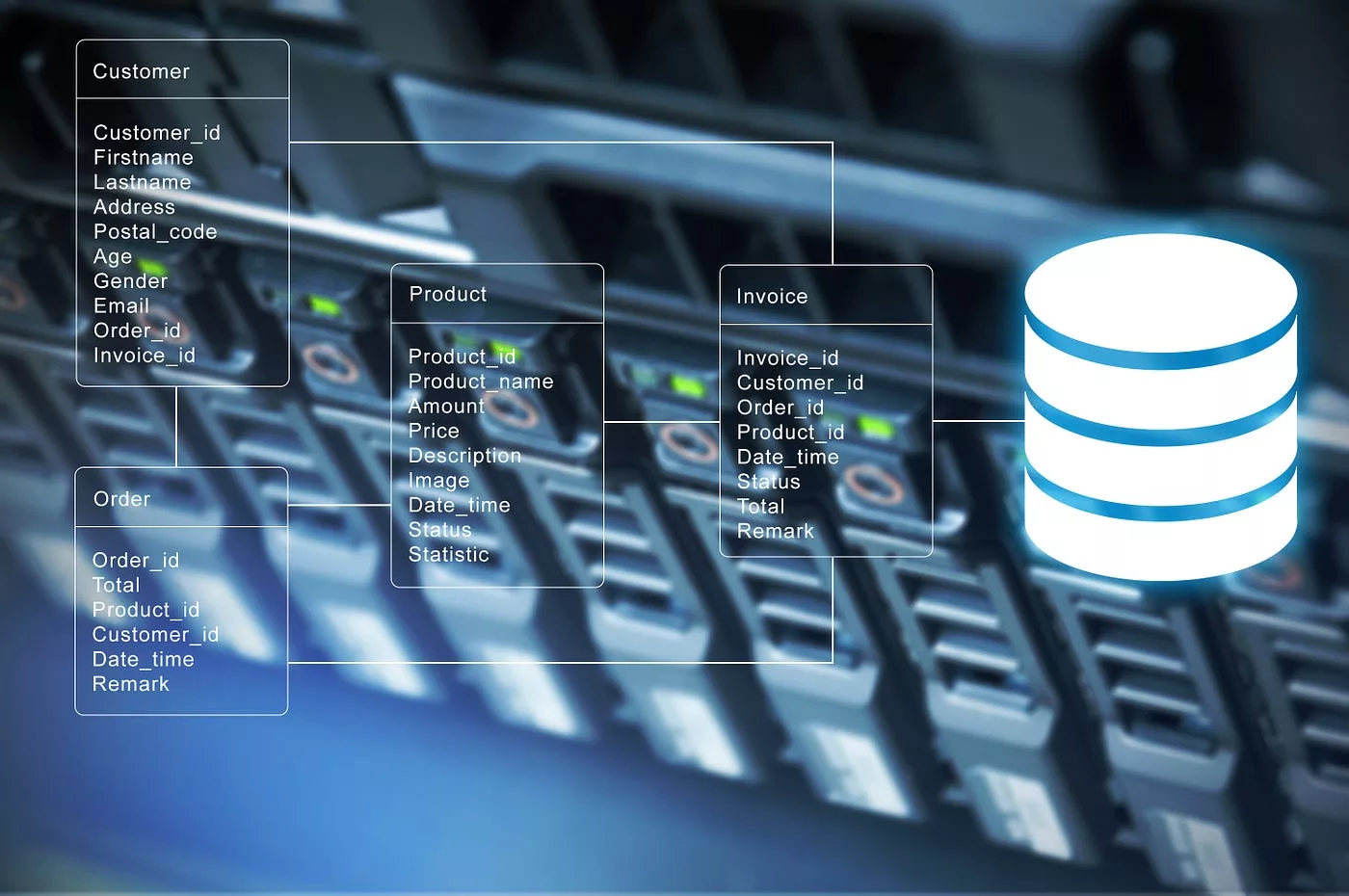
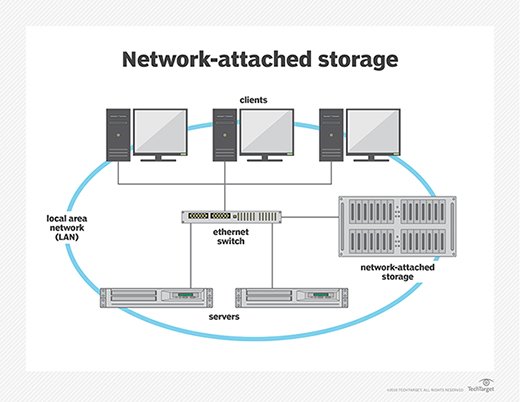
- SAN refers to a dedicated network architecture that enables the transfer of data between servers and storage devices, typically using block-level protocols like Fibre Channel or iSCSI. In the context of private and hybrid cloud infrastructure, SAN serves as a high-performance storage solution for applications and workloads requiring fast, reliable access to data.
2. How is SAN used in private cloud infrastructure?
- In private cloud infrastructure, SAN provides centralized storage resources accessible to cloud-based applications and services hosted within the organization’s data center. SAN facilitates high-speed data access, data sharing, and data protection for virtualized servers, databases, and other critical workloads in the private cloud environment.
3. What are the benefits of using SAN in private cloud infrastructure?
- Performance: SAN offers high-speed data transfer rates and low-latency access to storage, making it suitable for demanding workloads and performance-sensitive applications in private cloud environments.
- Scalability: SAN solutions can scale storage capacity and performance independently to accommodate growing data demands and changing workload requirements.
- Data Protection: SAN architectures typically include features like RAID configurations, snapshots, and replication for data protection, ensuring business continuity and data integrity in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
- Consolidation: SAN allows for the consolidation of storage resources across multiple servers or virtual machines, optimizing storage utilization and simplifying management in private cloud deployments.
4. How does SAN integrate with hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- In a hybrid cloud environment, SAN can be extended to public cloud platforms through dedicated network connections or cloud storage gateways. This enables seamless data migration, replication, and synchronization between on-premises SAN infrastructure and cloud-based storage services, providing flexibility and data mobility in hybrid cloud deployments.
5. What are the use cases for SAN in hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- Disaster Recovery: SAN-based replication solutions can replicate data from on-premises SAN infrastructure to cloud storage for disaster recovery purposes, ensuring data availability and business continuity in the event of site failures.
- Data Migration: SAN solutions facilitate the seamless migration of data between on-premises infrastructure and public cloud platforms, enabling organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud storage while maintaining data consistency and integrity.
- Bursting: SAN-enabled hybrid cloud deployments allow organizations to scale storage resources dynamically by offloading peak workloads or overflow data to the cloud, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
- Compliance and Data Governance: SAN-based replication and data synchronization capabilities support compliance requirements by ensuring data consistency, integrity, and retention across hybrid cloud environments, regardless of the location of data processing or storage.