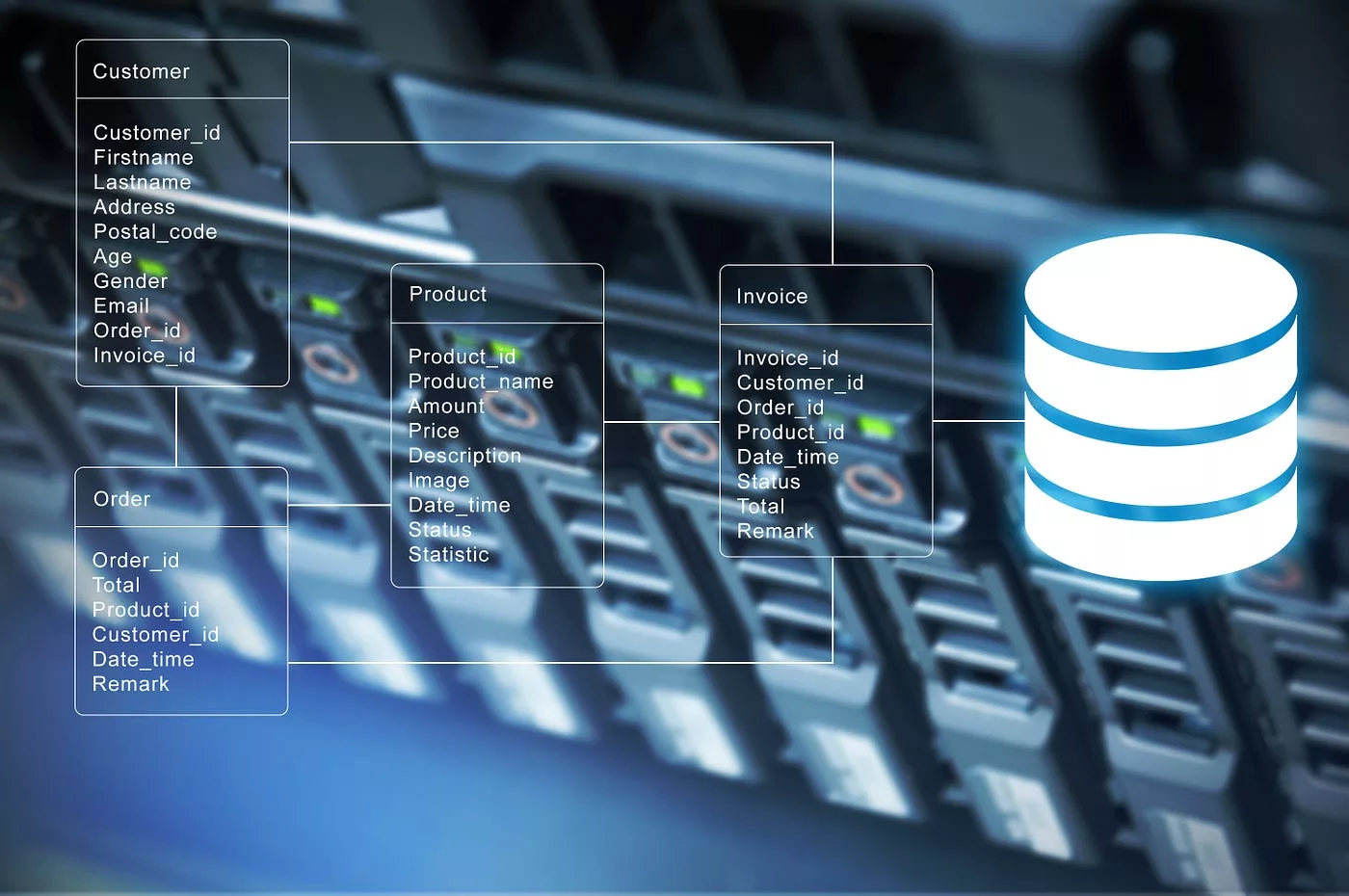
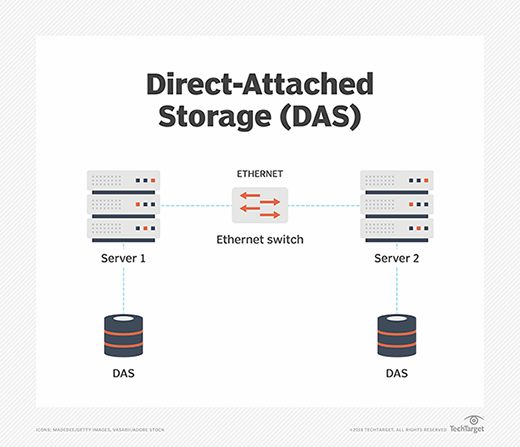
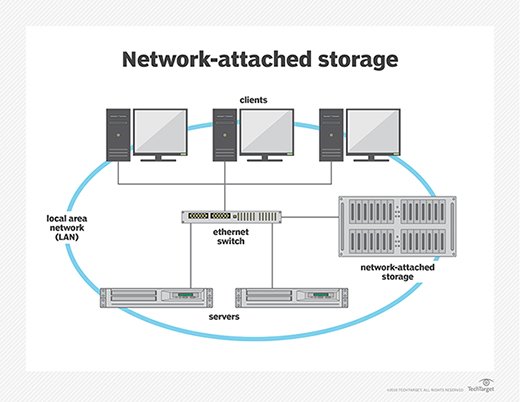
Laptop memory and local data resources may not be sufficient for enterprise applications for storage, memory protection, multiple inputs, multiple outputs, or speed and performance. As a result, most businesses use a SAN in conjunction with internet storage (NAS) to improve efficiency and data management.
Previously, only a small number of storage systems could VPN with servers, limiting the storage capacity of a network. On the other hand, A SAN adds networking flexibility by allowing one server, or a group of heterogeneous servers spread across various data centers, to share a shared storage resource. The SAN minimizes bandwidth bottlenecks by eliminating the typical dedicated network between a file server with storage and the assumption that the server essentially owns and oversees the storage devices. To improve storage, a SAN removes single points of failure.
Because a network may comprise many storage devices, such as disc, magnetic tape, and optical storage, a SAN is also ideal for disaster recovery (DR). It’s also possible that the storage utility isn’t close to its servers.
The SAN frees a storage device from being assigned to a specific server bus. It connects storage to the network directly, allowing it to be externalized or functionally dispersed across the company. The SAN also centralizes storage devices and server clustering, allowing for easier and more cost-effective centralized administration and a lower cost of ownership.
SANs, which typically use block-level storage systems, let data-moving applications perform better by sending data straight from the source to the target with minimal server intervention.
On the other hand, organizations are free to employ any network file system (NFS) that is appropriate for their infrastructure. SANs also allow many hosts to access numerous storage devices linked to the same network in current network topologies. A SAN can provide the following advantages:
- Application availability has been improved.
- For greater dependability, availability, and serviceability, storage exists regardless of applications and is accessed via many channels.
- Application performance that is improved
- Storage area networks (SANs) offload and relocate storage operations from servers to different networks.
- Consolidated and central
- Simplified management, scalability, flexibility, and high availability are available with SANs.
- Transfers data and vaulting from a remote location
- SANs protect the data from disasters and malicious assaults with a remote copy.
- Management that is simple and centralized
By producing individual images of storage medium, SANs make management easier.
A SAN, also known as the network behind servers, is a communications network that offers physical connections and allows any device to bridge across the network, utilizing interconnected parts like switches and directors. The storage area network (SAN) can also be considered an expansion of the memory bus idea. This concept allows storage devices or servers to communicate with one another via similar elements, including local area networks ( LAN (LANs) or wide-area networks (WANs) (WANs). A management layer organizes the connections, storage elements, and computer systems in a SAN, and this layer ensures that data exchanges are secure and reliable.
SANs enable high performance and availability gains by introducing new connecting storage to servers. They connect shared disk arrays and tape drives to numerous servers utilized for failover by clustered systems. They can also get around standard network traffic constraints in three methods, allowing for direct, high-speed transferring data between servers:
From the server to the storage
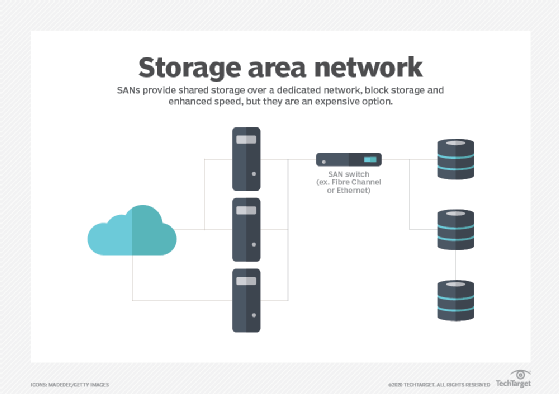
Image Source: Link
The advantage of this traditional interaction style is that several servers can access the same storage device serially or simultaneously.
From one server to another
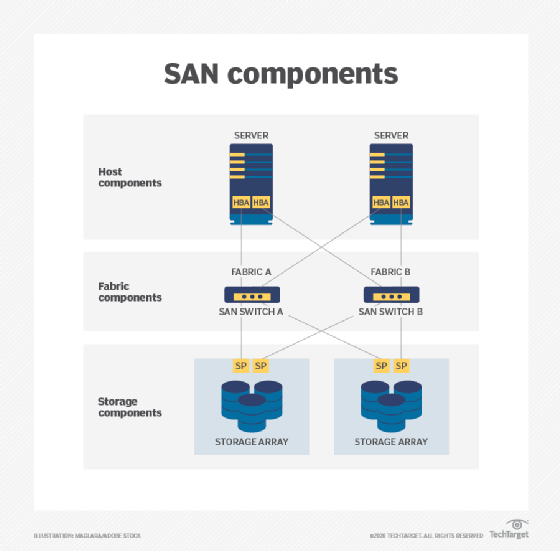
Image Source: Link
A storage area network (SAN) can be used for high-volume, low-latency communications between servers.
From one storage to the next

Image Source: Link
The capacity to move information without using a server frees up processor cycles on the server for other tasks, such as the submission of applications. Two examples are a disc drive device that backs up its information to a tape medium without needing a server or a secure remote mirror across the SAN.
The SAN switch is at the heart of most storage area networks, and its main function is to transport storage data among computers and shared storage systems. To construct a SAN, a switch joins numerous host servers made up of memory servers. Some switches can create a rudimentary SAN fabric as a stand-alone device, while others can be linked together to create a bigger SAN fabric.
SAN fabrics are multi-SAN switch interconnections that are active, intelligent, and non-shared. They expand the number of connections that you can make it in a SAN. Network Storage host bus adapters (HBA) connect switches and file servers.
The fundamental rationale for all SAN systems is the server infrastructure, which consists of various server platforms. With projects like server consolidation, you can get a lot done in a short amount of time.
SAN for Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning:
Big data analytics and machine learning require high-performance storage systems capable of handling large datasets and complex computations. SAN provides the necessary scalability, throughput, and low latency required for these demanding workloads. With SAN, organizations can efficiently process and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling valuable insights and informed decision-making.
SAN Applications in High Performance Computing (HPC):
High-performance computing relies on powerful infrastructure to perform complex calculations and simulations. SAN offers high-speed data transfer and parallel access to storage resources, making it an ideal choice for HPC environments. It provides the necessary bandwidth and low latency required to meet the stringent performance requirements of scientific research, financial modeling, weather forecasting, and other computationally intensive applications.
SAN for Video Streaming and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
In the age of online media consumption, video streaming and content delivery networks require fast and reliable storage solutions. SAN enables efficient storage and delivery of video content by providing high throughput and low latency access to multimedia files. With SAN, organizations can deliver high-quality streaming experiences to users while efficiently managing and distributing multimedia content across their networks.
SAN in Scientific Research and Data Centers:
Scientific research and data centers deal with vast amounts of data generated from experiments, simulations, and observations. SAN provides a scalable and robust storage solution that ensures data integrity, accessibility, and performance. It enables efficient data sharing, collaboration, and analysis, empowering researchers and scientists to accelerate their discoveries.
SAN Solutions for the Media and Entertainment Industry:
The media and entertainment industry relies heavily on storage systems capable of handling large media files, such as high-resolution videos, audio files, and graphics. SAN solutions offer high-speed storage access, enabling smooth editing, rendering, and distribution of media content. It also supports collaborative workflows, allowing multiple users to access and work on media files simultaneously.
SAN Benefits in High Throughput Data Services:
SAN brings several benefits to high throughput data services:
- Scalability: SAN allows organizations to easily scale storage capacity and performance to meet growing data demands.
- Performance: SAN provides high-speed data access and low latency, ensuring efficient data processing and analysis.
- Data Availability: SAN offers features such as redundancy, data replication, and snapshot capabilities, ensuring data availability and resilience against hardware failures.
- Centralized Management: SAN simplifies storage management through centralized administration, enabling efficient allocation of resources and streamlined operations.
- Cost Efficiency: SAN helps optimize storage utilization and reduces hardware and maintenance costs, providing a cost-effective solution for high throughput environments.
Ensuring Data Availability and Reducing Latency:
In high throughput data services, data availability and reduced latency are critical. SAN addresses these requirements through features like RAID configurations, redundant components, and high-speed interconnects. By implementing SAN-based storage architectures with redundant paths and efficient data replication, organizations can ensure continuous data availability and minimize latency.
FAQs on SAN Applications in High Throughput Data Services:
1. What are high throughput data services, and how does SAN facilitate their operation?
- High throughput data services involve the rapid and efficient processing of large volumes of data, often in real-time or near-real-time. SAN (Storage Area Network) plays a crucial role in these services by providing fast, reliable, and scalable storage infrastructure capable of handling the high data transfer rates required by throughput-intensive workloads.
2. What types of industries or sectors benefit from high throughput data services supported by SAN?
- Industries such as finance, healthcare, scientific research, telecommunications, and media and entertainment heavily rely on high throughput data services enabled by SAN. These sectors leverage SAN infrastructure to process and analyze vast amounts of data generated from financial transactions, medical imaging, scientific simulations, telecommunications networks, and multimedia content.
3. How does SAN contribute to achieving high throughput in data-intensive applications?
- SAN offers several features and capabilities that contribute to achieving high throughput in data-intensive applications:
- High-Speed Connectivity: SAN leverages high-speed networking technologies such as Fibre Channel or Ethernet with RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) to ensure low-latency, high-bandwidth communication between servers and storage devices.
- Parallelism: SAN architectures support parallel data access and I/O operations, allowing multiple servers or applications to access storage resources simultaneously, thus maximizing throughput.
- RAID Configurations: SAN systems often utilize RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations to distribute data across multiple disks, improving both performance and fault tolerance.
- Caching and Tiering: SAN solutions may incorporate caching and tiering mechanisms to optimize data placement and access patterns, ensuring that frequently accessed data is stored in high-performance tiers for faster retrieval.
4. What are some examples of high throughput data services that rely on SAN infrastructure?
- Big Data Analytics: SAN-based storage solutions are essential for storing and processing large datasets used in big data analytics applications. SAN facilitates high-speed data ingestion, processing, and querying, enabling organizations to derive insights and make data-driven decisions in real-time.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): SAN infrastructure supports high-throughput data access and storage requirements in HPC environments used for scientific simulations, engineering modeling, and computational research.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs leverage SAN storage to store and distribute large volumes of multimedia content, such as videos, images, and streaming media, to users worldwide with low latency and high throughput.
- Financial Trading Platforms: SAN-based storage solutions provide the high-speed data access required by financial trading platforms for processing market data, executing trades, and maintaining transactional integrity with minimal latency.
- Telecommunications Networks: SAN infrastructure supports high-throughput data services in telecommunications networks for handling voice, video, and data traffic, ensuring reliable and low-latency communication services for end-users.
5. How can organizations optimize SAN infrastructure for maximum throughput in data-intensive environments?
- Performance Tuning: Fine-tune SAN configurations, including storage arrays, network switches, and host systems, to optimize performance parameters such as I/O queue depths, block sizes, and caching settings.
- Network Optimization: Implement high-speed network fabrics with low-latency switches and high-bandwidth interconnects to minimize data transfer bottlenecks and ensure efficient communication between servers and storage.
- Workload Optimization: Analyze workload characteristics and access patterns to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize data placement, caching strategies, and RAID configurations to maximize throughput.
- Scalability: Scale SAN infrastructure horizontally by adding additional storage arrays, network switches, or host connections to accommodate growing data volumes and increasing throughput requirements over time.
- Monitoring and Analysis: Deploy monitoring tools to continuously monitor SAN performance metrics, identify performance anomalies or bottlenecks, and proactively optimize SAN configurations for maximum throughput and efficiency