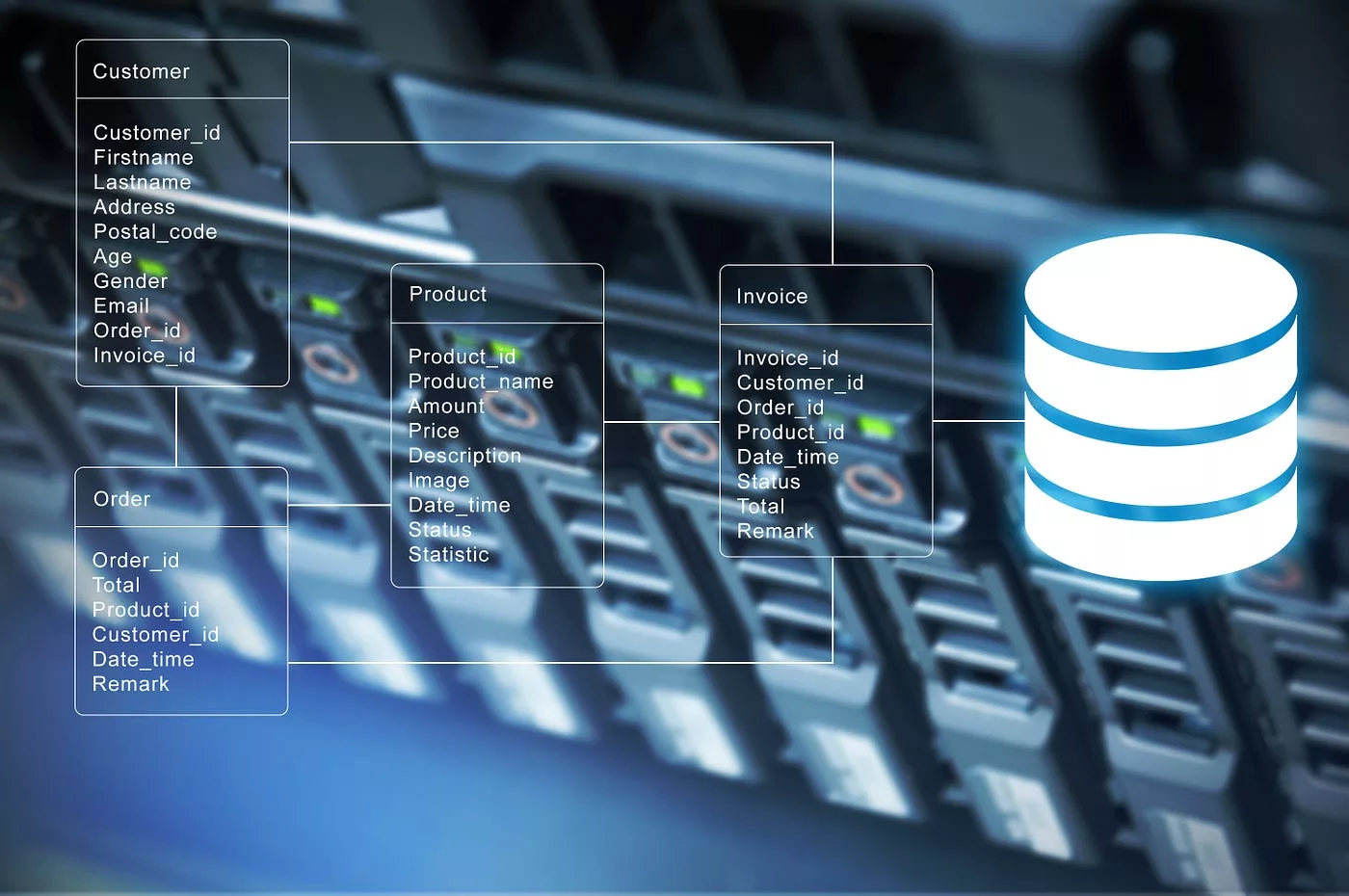
Vendors are working to make NAS infrastructures compatible with cloud services as enterprises study cloud services. One hurdle in the public cloud is that file-based apps operating on NAS must be updated to use storage solutions, the most prevalent storage method in cloud services. Rewrites of applications can be meaningful and costly. Even though cloud computing has a reduced computation cost, adoption is hampered when there is a cost and a long lead time for deploying applications.
Companies like OrangeFS, TurnKey Linux, and Red Hat are vying for Amazon Services (AWS) clients by offering system files that don’t necessitate application rewrites. OrangeFS, for example, has a high-performance computing (HPC) file system.
Engineer modeling programs, biotech testing, and weather modeling are common uses.
TurnKey allows you to deploy NAS on AWS easily, but it lacks capabilities like snapshot and remote replication. Red Hat Storage Server enables local synchronous replication across Network Segments and asynchronous replication across regions, allowing you to implement NAS in AWS. If a zone fails, this feature ensures business continuity and disaster recovery if an AWS region fails.
Although the company claims it’s on its to-do list, snapshots aren’t supported by Red Hat Storage Server. The AWS Marketplace Place offers full service and Red Hat Hard Disk storage.
OpenStack is gaining traction as a private cloud option to VMware-based personal cloud infrastructure. You can choose your server’s virtualization and file or object storage provider using the OpenStack platform. Druva and SwiftStack are two storage startups worth checking out.
The InSync product from Druva manages data storage across numerous nodes (data centers). With Druva’s InSync, data duplication is possible, with only one copy of data retained for numerous nodes. Deduplication can dramatically reduce backup times. InSync uses 256-bit security socket layer (SSL) encryption for data in transit and 256-bit strong cryptographic standard (AES) for data storage.
SwiftStack, on the other hand, is an app object storage solution that serves information directly from storage rather than needing additional hardware Network services.
Red Hat Enterprise Store also offers files and object storage within the OpenStack platform. These storage capacity management suppliers use commodity hardware, allowing businesses to save money.
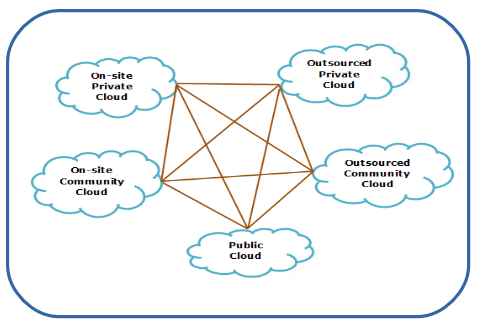
The Three Types of Clouds: Private, Commercial, and Hybrid
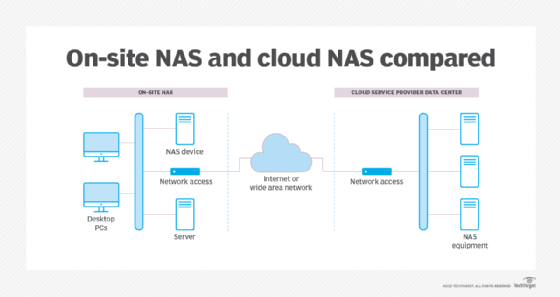
Image Source: Link
Like Aws, Azure, Cloud Platform, and Cloud Platform, a public cloud hosts a public cloud. It offers pay-as-you-go on-demand services through the public Internet. Several organizations use public cloud resources at the same time.
On the other hand, a private cloud is often adapted to the specific of a single company and is often custom-built to match a specific architecture and use case. It can be stored on-premises or even in a data center where it is colocated.
At a minimum, one public and a private cloud make up a hybrid cloud. You could also have a unique, virtualized on-premises environment linked to the public cloud. While this does not meet the NIST description of the hybrid cloud, most of the same issues apply.
While this does not meet the NIST description of the hybrid cloud, most of the same issues apply.
Use Cases for Private Clouds
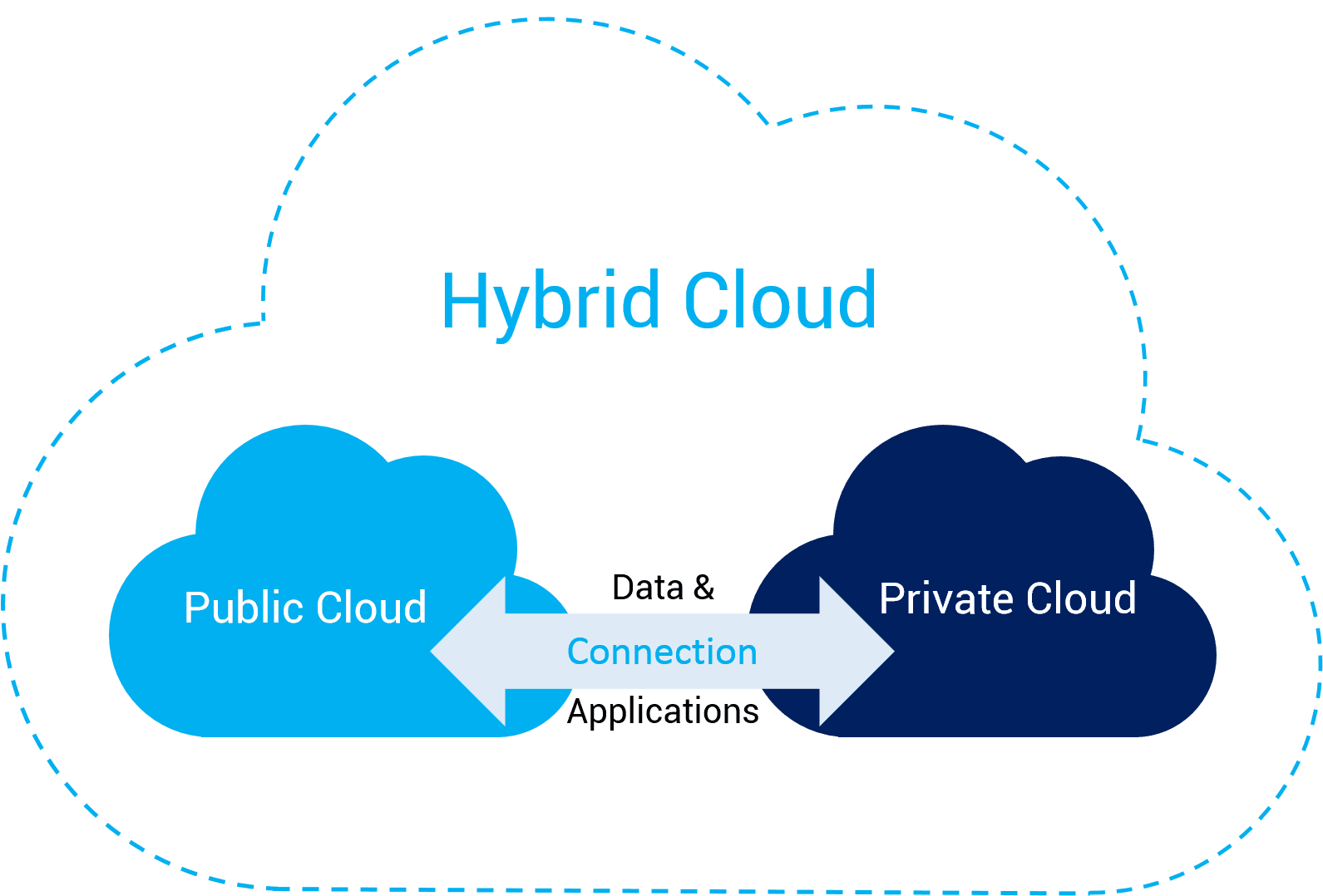
Image Source: Link
Many businesses utilize public clouds, which offer advantages such as enhanced availability and the capacity to scale to meet fluctuating demand. However, private clouds are a preferable alternative in some cases:
Requirements for specialized hardware or configuration

Image Source: Link
A cloud provider cannot deliver the hardware or architecture that a specific application requires in some circumstances. If your workload necessitates an emulator (VM) with a semi CPU and RAM architecture or an os that no public cloud provider supports, moving to a secure cloud may be your only realistic alternative.
Regulatory or Governance Requirements

Image Source: Link
In other circumstances, corporations are forced to use a private cloud due to security or governance concerns. Certain governments demand that application data relating to residents of that country be kept within the country.
Use Cases for Hybrid Cloud

Image Source: Link
While cloud storage can be persuasive in some circumstances, organizations occasionally involve a mix of these advantages and the benefits of public clouds. In some situations, a hybrid cloud might be the superior option:
Workloads that haven’t been tested
It’s not always evident how successful an application will be in the market. “Fail fast, fail cheaply” is a philosophy many cloud-based enterprises follow. In light of this guidance, it stands for businesses to employ cloud infrastructure services for a new, unproven application before investing in the capital costs of debuting a cloud infrastructure. Once an organization has established a stable workload pattern and can see a clear path to the business’s long-term viability,
The bursting of clouds
To meet capacity demands, workloads are “spilled over” to a different cloud environment known as cloud bursting. This is typically a transient circumstance, such as a traffic increase due to seasonality visitation or a news item that temporarily pushes visitors to a specific application. Our customers use the expression “purchase the base, lease the spike” to describe a cloud bursting use case. In this hybrid cloud scenario, a fixed private cloud environment handles the steady-state, while on-demand resources from the public cloud manage the spike.
File Sharing and Collaboration with NAS in Private and Hybrid Clouds
NAS systems can be easily and securely deployed in both private-sector (onsite) and hybrid cloud environments. They are ideal for providing solutions to organizations that need centralized storage, secure access, scalability, and manageability. By leveraging the power of a NAS system within either environment, users can take advantage of features such as file sharing and collaboration; capacity expansion on demand; scalabile storage server performance; content archiving capabilities; enhanced mobility through wireless networks; consolidated email services via flexible IMAP4 support; plus they have the resources necessary for backup/restore, replication server consolidation strategies.
In addition to the above-mentioned benefits, a NAS system provides rapid data protection due to its high fault tolerance built into the architecture. Moreover, with built-in virus scanning capabilities, a NAS system can monitor files up to date and prevent downloads from external sources or removable devices connected to the network, thereby protecting valuable company information from malicious viruses or external attackers.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Using NAS in Cloud Environments
The days of storing data on external hard drives or flash drives are long gone. With the emergence of cloud storage technologies, many businesses have shifted to a process known as Network Attached Storage (NAS). NAS is an automated system that permits easy and efficient access to large amounts of data over the internet. For organizations dealing with huge volumes of information, NAS provides reliable and secure systems for backing up sensitive documents and other important files. It also helps protect their information from cyber-attacks or natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes, earthquakes etc., by providing redundancy through multiple locations in the cloud environment.
Aside from being extremely convenient when it comes to backups and disaster recoveries (DR), NAS also has several features which further add to its utility. It includes
- Encryption capabilities,
- Configurable storage policies and permissions that help maintain organizational compliance standards;
- Scalability options which allow IT teams more freedom when synchronizing new systems;
- Improved performance thanks to better server utilization;
- Safe deletion processes which ensure total erasure of confidential copies stored within the storage system after backup creation period expires;
- Media streaming tools for faster sharing among network devices;
- Plus countless other services tailored specifically for specific enterprise needs.
Scalability and Performance Benefits of NAS in Private and Hybrid Clouds
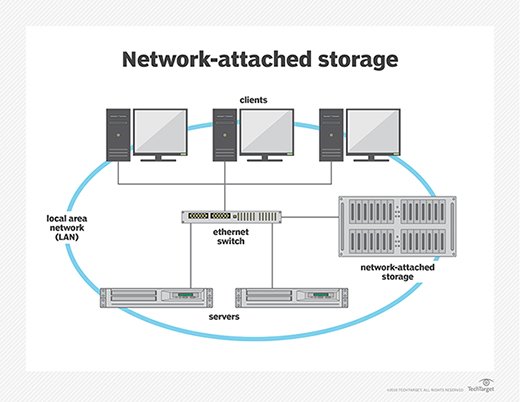
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a distributed file system that allows multiple users and applications to access shared files simultaneously. As more organizations migrate their compute resources into cloud deployments like Microsoft Azure, AWS or Google Cloud Platform, NAS solutions offer several advantages in terms of scalability and performance for private and hybrid cloud architectures.
With NAS, all the devices connected over the same network can have access to the same data without having to replicate them on each device. This helps reduce overall storage costs and manage capacity better as well as open up possibilities for semantic search across multiple servers from a single source. Such systems also offer the advantage of reduced latency, as local caching mechanisms optimize performance during peak usage periods without compromising data availability.
Furthermore, installing additional drives in the NAS cluster help balance load between nodes which increases throughput; it also offers enhanced security options since no individual node contains mission-critical information at any given time so if one node fails there’s less risk of incurring operational downtime due to resulting outages or disruptions in services provided by other nodes within the cluster.
Centralized Storage Management with NAS in Cloud Infrastructure
NAS (Network Attached Storage) offers cloud infrastructure users the opportunity to manage storage from a centralized location. In this approach, all of the servers within an organization can access their NAS for file sharing and data sorting purposes. It is also possible to access the same files concurrently among multiple organizations as well.
One advantage that comes with Network Attached Storage over traditional on-premises storage methods is its scalability and flexibility. By utilizing automated processes, such as incremental or differential backups, IT administrators are able to quickly grow disk capacity while continuing operations in real time. Data redundancy and protection are two other powerful characteristics of NAS systems, which help keep your information secure against disaster scenarios like ransomware attacks or natural disasters that have wiped out local hard drives before.
Last but not least, NAS solutions enable quick deployment without having any physical hardware on site along with improved business continuity through remote access capabilities anytime anywhere by end users or designated support personnel’s devices if needed be during unforeseen emergency events
Security and Data Protection Considerations for NAS in Private and Hybrid Clouds
The use of Network Attached Storage (NAS) for private and hybrid clouds presents security and data protection considerations. Cloud users must be aware that any type of storage carries some risk, regardless of the technology used. Data stored on NAS devices is subject to similar risks as with any other networked device, including unauthorized access, malware infection, and failure or loss due to hardware or software malfunctions.
This means it is important to properly secure all elements associated with the NAS solution, including both physical and virtual components.In addition to securing traditional vulnerabilities such as authentication protocols and encryption systems, cloud-based NAS solutions also present different challenges when it comes to data privacy compliance and disaster recovery planning.
For instance, organizations must understand the storage location of their data to comply with regional privacy law regulations. This understanding may necessitate implementing additional security layers beyond the default offerings when deploying new cloud-based systems or related services such as Amazon S3 or Microsoft AzureBlob Storage™ (Azure). Additionally, users must determine how their organization will handle digital disaster scenarios since most commercial services do not include a backup process other than restoring from an offsite location after an outage occurs.
Integration of NAS with Virtualization Technologies in Cloud Environments
The integration of network attached storage (NAS) into virtualization technologies such as hypervisors, provides a cost effective solution to provide shared and secure access to corporate data stored in the cloud. This enables deployment of enterprise applications that can seamlessly access critical business information from any location or device. Additionally, the incorporation of NAS technology with virtualization capabilities helps maximize server usage and increase productivity.
It also allows for easy scalability when needing extra capacity to store more data while providing automated failover options for continuous operations in case of outages or hardware issues. Furthermore, businesses gain increased flexibility, security and control over their distributed environment through utilization of multiple dedicated physical servers combined with advanced storage systems built on top of existing infrastructure components.
FAQs on NAS Applications in Private and Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
1. What is NAS (Network Attached Storage) in the context of cloud infrastructure?
- NAS refers to a storage device that is connected to a network and provides file-based storage services to other devices on that network. In the context of private and hybrid cloud infrastructure, NAS serves as a centralized storage repository accessible to cloud-based applications and services.
2. How is NAS used in private cloud infrastructure?
- In private cloud infrastructure, NAS serves as a scalable and efficient storage solution for storing application data, user files, and other digital assets. It provides shared access to data across multiple servers or virtual machines within the private cloud environment.
3. What are the benefits of using NAS in private cloud infrastructure?
- Scalability: NAS systems can easily scale storage capacity to accommodate growing data demands.
- Centralized Management: NAS allows for centralized management of storage resources, simplifying administration tasks.
- High Availability: NAS systems often include features like redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure high availability of data.
- Cost-Effectiveness: NAS solutions typically offer a cost-effective storage option compared to traditional SAN (Storage Area Network) solutions.
- Flexibility: NAS supports various protocols and can be integrated with different operating systems and applications.
4. How does NAS integrate with hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- In a hybrid cloud environment, NAS can be deployed both on-premises and in the cloud. This allows organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud storage while maintaining control over certain data or applications on-premises. NAS facilitates seamless data synchronization and access between on-premises infrastructure and cloud instances.
5. What are the use cases for NAS in hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: NAS can be used to store backup data on-premises and replicate it to the cloud for disaster recovery purposes.
- Collaboration and File Sharing: NAS provides a centralized platform for teams to collaborate and share files across on-premises and cloud environments.
- Archive Storage: NAS systems can be used to archive infrequently accessed data, with the flexibility to store archived data either on-premises or in the cloud.
- Media and Content Delivery: NAS is well-suited for storing media files and content that need to be accessed by distributed users or applications across hybrid cloud environments.
6. How does security work with NAS in private and hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- Security measures such as access control lists (ACLs), encryption, and authentication mechanisms are implemented to protect data stored on NAS systems in private and hybrid cloud environments. Organizations should also follow best practices for network security and data governance to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
7. What considerations should be taken into account when deploying NAS in private and hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- Performance Requirements: Assess the performance needs of applications and workloads to determine the appropriate NAS solution.
- Data Protection: Implement backup, replication, and disaster recovery strategies to safeguard data stored on NAS systems.
- Compliance Requirements: Ensure that NAS deployments adhere to regulatory compliance standards relevant to your industry.
- Scalability: Choose NAS solutions that can scale to accommodate future growth in data storage requirements.
- Integration: Consider the compatibility of NAS systems with existing infrastructure, cloud platforms, and applications.
8. How can I ensure data availability and resilience with NAS in hybrid cloud infrastructure?
- Utilize redundancy features such as RAID configurations and data replication across geographically dispersed locations to ensure data availability and resilience.
- Implement automated failover mechanisms to switch to secondary NAS instances or cloud storage in case of primary system failures.
9. Can NAS be integrated with other cloud services in hybrid environments?
- Yes, NAS can be integrated with other cloud services such as object storage, backup services, and content delivery networks (CDNs) to enhance data management, protection, and distribution capabilities in hybrid cloud environments.
10. What are some popular NAS solutions suitable for private and hybrid cloud infrastructure?
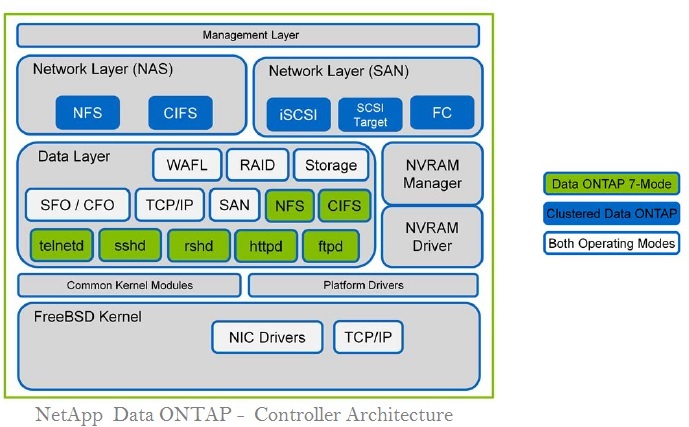
- Popular NAS solutions include NetApp ONTAP, Dell EMC Isilon, Synology DiskStation, QNAP NAS, and FreeNAS. These solutions offer a range of features and scalability options suitable for various private and hybrid cloud deployment scenarios